Techniques to Increase Tire Traction
Modern tire design must account for complex interactions between rubber compounds, tread patterns, and road surfaces across diverse operating conditions. Field measurements show that even minor changes in compound formulation can alter friction coefficients by 0.1-0.2, while tread design variations can affect wet grip performance by up to 30% under identical conditions.
The fundamental challenge lies in simultaneously optimizing rolling resistance, wet grip, and wear resistance—three properties that often work against each other in traditional tire design.
This page brings together solutions from recent research—including multi-zone tread compounds, advanced silica-based formulations, variable-depth sipe designs, and optimized steel cord configurations. These and other approaches demonstrate how manufacturers are achieving better traction performance while maintaining acceptable tire longevity and fuel efficiency.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
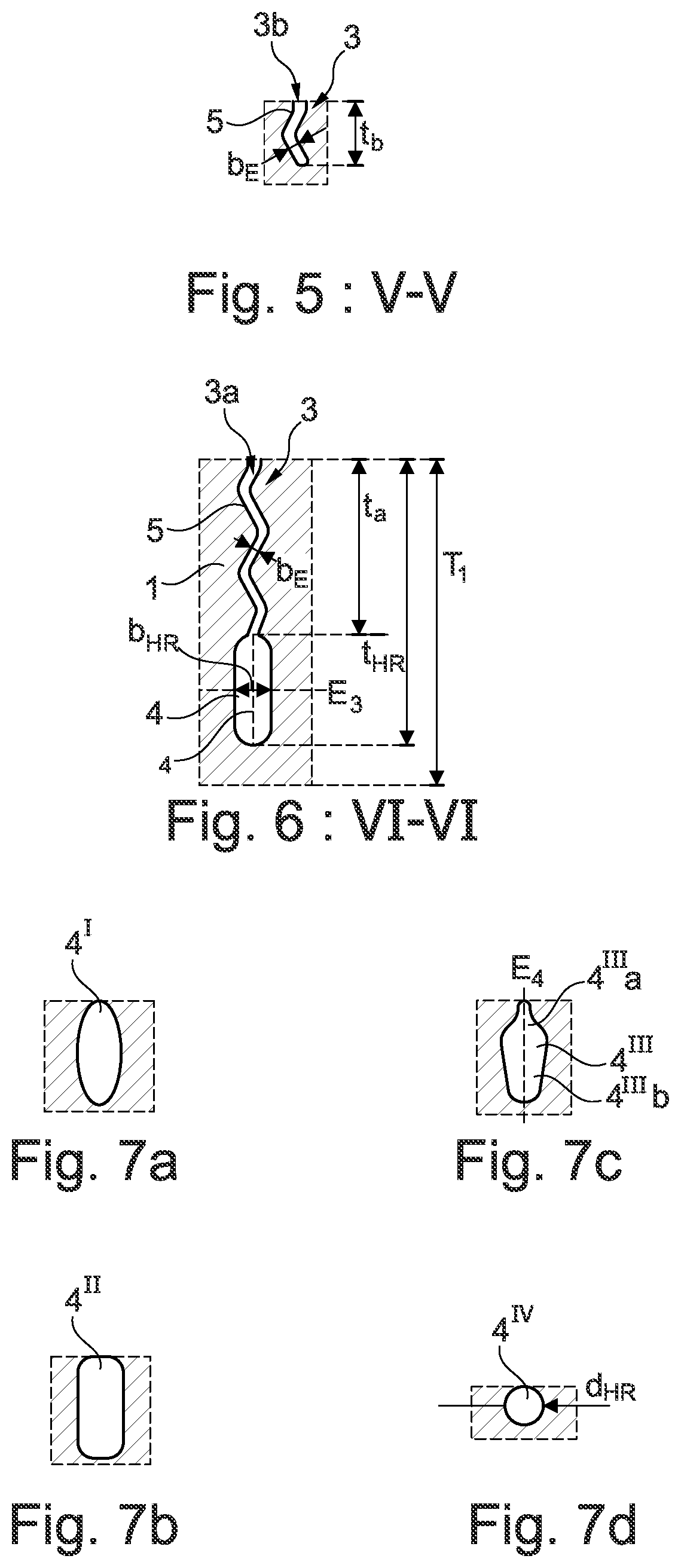
1. Engineered Polydiene Matrices and Silane Coupling Strategies
1.1. The Silica-Rubber Compatibility Challenge
Silica is the go-to filler for reducing hysteresis in passenger and truck tires. However, there's a fundamental compatibility problem: silica has a hydrophilic (water-loving) surface, while the rubber backbones used in tires—such as SBR, NR, or BR—are non-polar. This mismatch makes it difficult for the silica to bond effectively with the rubber matrix.
1.2. ExxonMobil's Epoxidized Polypentenamer Solution
Researchers at ExxonMobil Chemical (among the world's largest chemical divisions, producing petrochemicals and polymers for packaging, automotive, and healthcare applications) developed a clever solution using an epoxidized polypentenamer in-situ compatibilizer. The approach works by first oxidizing the cyclopentenamer chain, then optionally opening the epoxide rings to create vicinal diols. This process strategically places polar sites along the rubber backbone that can form hydrogen bonds with the silanol groups on the silica surface.
When formulators add 10–50 phr of this modified CPR alongside 10–200 phr of silica during conventional mixing, several benefits emerge. The approach reduces the need for external silane coupling agents, lowers VOC emissions, and improves key performance metrics including tensile strength, tear resistance, and abrasion life. Importantly, these improvements come without disrupting standard sulfur cure schedules used in tire manufacturing.
1.3. Bridgestone's Targeted Hydrosilyl Grafting Platform
While random epoxidation provides polarity to rubber backbones, it can be difficult to control precisely. Bridgestone (the world's largest tire manufacturer, parent of Firestone, offering a full range from passenger to OTR and specialty tires) developed a more targeted approach using a multisite hydrosilyl grafting platform.
The method uses specially designed TMDS-based grafting agents that come pre-loaded with polar groups like PEG, piperidine, or NTMS attached to vinyl substituents. These grafting agents react with SBR rubber chains through hydrosilylation at moderate temperatures of 50–80°C. The key advantage is that the siloxane core contains multiple Si–H bonds, allowing engineers to attach dozens of polar grafting points along the rubber backbone without increasing molecular weight or causing unwanted cross-linking.
Performance Benefits of SBR-g-TMDS Products
The resulting SBR-g-TMDS products show improved tire performance in two key areas. Rolling resistance decreases because the grafted polar groups couple more effectively with silica fillers. Wet grip also improves because the grafts alter the glass-transition behavior of the rubber matrix, optimizing its mechanical properties for better road contact.
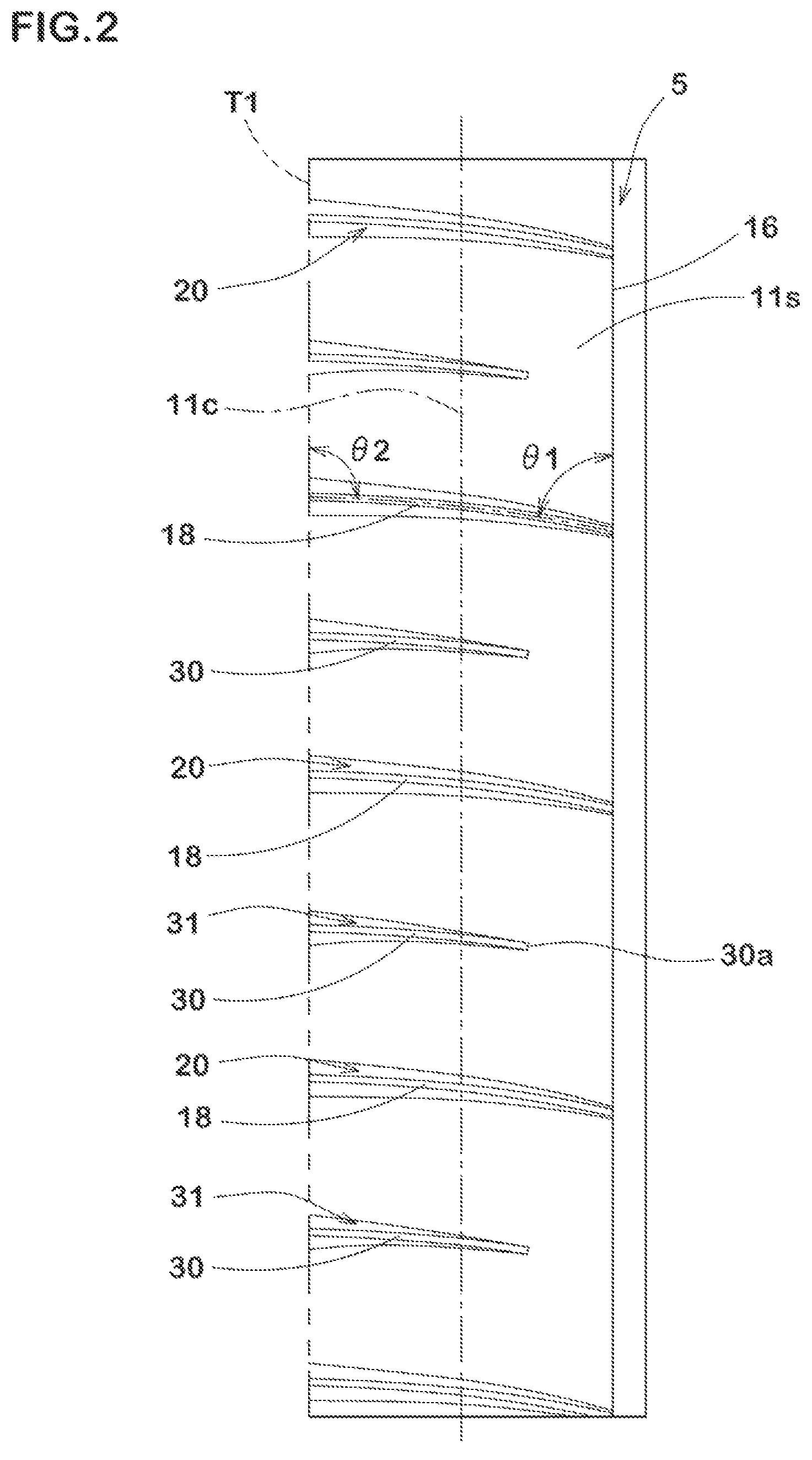
1.4. Dual-Functional Nitrogen-Enhanced Architecture
Bridgestone took this approach even further by incorporating nitrogen-bearing groups. Their multifunctional silylated polydiene architecture creates a dual-purpose system where one site forms covalent bonds with silica particles while a secondary site provides additional hydrogen-bonding or acid-base interactions. This dual-functional approach leads to better filler dispersion throughout the rubber matrix and reduces energy loss during tire flexing (hysteresis). Surprisingly, the technology also delivers an unexpected benefit: improved traction on snow-covered roads, likely due to the way the nitrogen groups interact with moisture and ice crystals.
1.5. Built-in Coupling Through Functional Comonomers
Another approach involves building the coupling chemistry directly into the polymer during its formation. Researchers developed dual-siloxy functional diene comonomers that can be copolymerized with butadiene and, optionally, styrene. This creates polydienes with functional groups strategically placed at the chain ends (alpha and omega positions) or along the backbone itself.
Strategic Design Features
The design includes at least one bulky trialkyl-siloxy group (-OR substituent) attached to each comonomer. This bulky group serves a dual purpose: it provides the desired functionality while keeping the polymer's Mooney viscosity low and maintaining a narrow molecular-weight distribution. These properties are crucial because they make the resulting polymer easier to mix and extrude during tire manufacturing.
After polymerization, manufacturers can fine-tune the polymer's polarity by converting the siloxy groups to hydroxyl or metal-alkoxide groups. This post-polymer modification allows precise control over how the rubber interacts with silica fillers. The result is improved performance across multiple metrics: reduced Payne effect (better filler dispersion), balanced wet grip for safety, and superior rolling resistance for fuel efficiency.
1.6. Goodyear's Practical Implementation
These chain-level modifications come together in practical tire formulations. Researchers at Goodyear (one of the largest U.S. tire manufacturers, producing consumer, commercial, aviation and racing tires; also famous for the Goodyear Blimp) developed a silica-coupling low-Tg SBR blend that demonstrates how these technologies work in practice. The formulation starts with a polyisoprene matrix (70–95 phr) that provides excellent wear resistance. To this base, they add a smaller amount of highly functional low-Tg SBR (5–30 phr) along with silica filler (40–80 phr). The functional SBR acts as a bridge between the polyisoprene matrix and the silica particles, optimizing how they interact. This approach delivers the best of both worlds: truck tires that reduce fuel consumption through lower rolling resistance while maintaining the wet-road safety and tread life that fleet operators demand.
1.7. Moving Beyond Molecular Interactions
Now that researchers have optimized how polymer chains interact with silica at the molecular level, the next challenge is controlling the physical structure of the silica network itself. While coupling agents and functional polymers solve the compatibility problem, the way silica particles connect and distribute throughout the rubber matrix also plays a crucial role in tire performance.
2. Silica Fractal Control and Carbon Nanostructures for Tunable Friction
2.1. Quantitative Silica Design Through Fractal Geometry
Tire engineers have long struggled with a fundamental trade-off: achieving high friction without sacrificing structural rigidity. The geometry of silica aggregates plays a crucial role in resolving this challenge. Toyo Tire (a Japanese tire company behind the Toyo and Nitto brands, noted for performance and off‑road products in the replacement market globally) developed a quantitative Dm/Rg silica design rule that uses a specific ratio to optimize both properties simultaneously.

The approach focuses on the ratio between mass-fractal dimension (Dm) and inertia radius (Rg). When this ratio is maintained at 0.20 nm⁻¹ or above in solution-polymerized S-SBR compounds, both wet grip and Shore-A hardness improve together. The key is using balanced silane coupling agents—whether sulfur-, amino-, ureido-, or isocyanato-based—to properly disperse these complex silica aggregates throughout the rubber matrix.
This careful dispersion strategy achieves two goals at once. It preserves a stiff filler skeleton that maintains tire handling characteristics, while simultaneously exposing hydrophilic surface areas that boost adhesion on water-lubricated pavement. The result is better wet-weather performance without compromising the structural integrity needed for precise steering and cornering.
2.2. Dynamic Strain-Adaptive Silica Networks
Moving beyond static aggregate control, Toyo Tire developed a more dynamic approach called strain-adaptive spacing. This method manipulates how silica clusters move and reorganize when the tire experiences different types of mechanical stress.
The technology starts with high-surface-area precipitated silica combined with a dual-silylation system that deliberately avoids sulfur-based coupling agents. The key innovation focuses on controlling a specific ratio called V50/V0—which compares the inertia radius of silica clusters after 50% elongation to their radius at rest. When this ratio reaches 1.30 or higher, something remarkable happens: the material forms a strain-adaptive silica network (V50/V0 ≥ 1.30) that behaves differently under different driving conditions.
Adaptive Performance Under Variable Load Conditions
During normal cruising, when the tire experiences relatively gentle deformation, the silica network stays dispersed and suppresses rolling hysteresis. This reduces energy loss and improves fuel efficiency. However, when the driver brakes hard or corners aggressively, the increased strain causes the silica clusters to re-aggregate, which raises friction exactly when it's needed most. The result is impressive performance metrics: wet-grip indices reach 125 while rolling-resistance indices drop to 71–80, all while maintaining structural integrity with hardness levels of 100–115 Shore A.
2.3. Plasma-Functionalized Carbon Reinforcement Systems
Carbon-based fillers offer an alternative to silica, but they face their own dispersion challenges. Researchers developed a plasma-functionalised graphene/CNT reinforcement system that addresses these limitations directly. The approach uses plasma treatment to graft amine or silane groups onto the surface of both graphene flakes and carbon nanotubes.
This surface modification solves the dispersion problem that typically plagues carbon fillers in rubber matrices. The grafted functional groups help the carbon particles distribute uniformly throughout butadiene-rich polymers, creating a percolated network structure. This network provides multiple benefits: it stiffens the rubber matrix for better handling, creates longer diffusion paths that protect against ozone degradation, and accelerates the vulcanization process without leaving behind metallic residues.
Performance Advantages of Carbon-Based Systems
The performance improvements are substantial. Tire treads made with this carbon reinforcement system deliver high grip on both wet and icy surfaces, longer abrasion life, and reduced overall tire weight. These benefits make the technology particularly attractive for applications where weight reduction and durability are critical factors.
2.4. Transitioning to Polymer Matrix Optimization
With both the chemical compatibility and physical structure of fillers now optimized, tire engineers can turn their attention back to the polymer matrix itself. The next step involves fine-tuning the glass-transition temperature (Tg) profile of the rubber to achieve the precise balance of flexibility and stiffness needed for different driving conditions.
3. Dual-Tg Polymer Systems Fine-Tuned with Resins and Plasticizers
3.1. Bimodal Glass-Transition Architecture for Heavy Electric Vehicles
Tire engineers continue to face the challenge of balancing three competing performance requirements: rolling resistance, wet grip, and wear resistance. This is particularly difficult for silica-filled S-SBR tread compounds used in modern tires.
Researchers at Hankook (a South Korean tire maker known for passenger, light truck and motorsport tires, supplying OEMs and replacement markets worldwide) developed a solution using a bimodal-Tg S-SBR matrix that strategically combines two different rubber types.
Dual Rubber Matrix Design
The approach blends 30–60 phr of very low-Tg S-SBR (with glass-transition temperatures from −70°C to −45°C) with 20–50 phr of medium-Tg S-SBR (ranging from −50°C to −20°C). This creates a rubber matrix with two distinct glass-transition regions that respond differently to temperature changes.
To fine-tune the material's mechanical properties, formulators add a dual resin package consisting of 5–30 phr high-Tg resin combined with 5–20 phr low-Tg resin.
Performance Benefits for Electric Vehicle Applications
This resin combination allows precise control over tan δ (the loss tangent that measures energy dissipation). The result is a tread compound that remains pliable enough for effective wet braking while staying cool during steady rolling conditions.
When combined with 80–110 phr of highly dispersible silica, 6–12 phr silane coupling agent, and a functionalized liquid polymer, the complete formulation delivers multiple performance improvements: reduced hysteresis for better fuel efficiency, improved wear resistance for longer tread life, and enhanced wet stopping power.
These qualities are particularly important for heavy, high-torque electric vehicles, which place unique demands on tire performance due to their instant torque delivery and substantial battery weight.
3.2. High-Load Terpene/C5 Resin Architecture for Enhanced Wet Performance
To push tan δ performance even further in the critical 0–5°C temperature range, tire formulators can significantly increase the total resin content. Goodyear developed a high-load terpene/C5 resin architecture that incorporates at least 55 phr of total resin into the rubber matrix.
Strategic Resin Blending Approach
The formulation typically combines 20 phr of terpene resin with 30 phr or more of C5 or C9-modified resin. This resin package is blended into two different SBR grades, both with glass-transition temperatures around −50°C.
The elevated levels of high-Tg resins strategically boost hysteresis in the wet-braking frequency band, where increased energy dissipation translates to better grip on wet roads. Meanwhile, the dominant low-Tg SBR component continues to control tan δ at 60°C, maintaining low rolling resistance during normal driving conditions.
High-Silica Network Structure
To complete the network structure, formulators add a substantial silica loading of 135–200 phr. This high-resin, high-silica combination produces tire treads that achieve superior EU wet grip labels while simultaneously delivering lower rolling resistance compared to conventional silica/SBR systems. The result is a tread compound that outperforms traditional formulations in both safety and fuel efficiency metrics.
3.3. Aluminum Hydroxide Heat Management Systems
Tire engineers can further optimize dual-Tg systems by incorporating aluminum hydroxide as both a reinforcing agent and thermal management component. Goodyear came up with aluminium-hydroxide/hydrocarbon-resin synergy solution that addresses both mechanical performance and heat dissipation simultaneously.
Dual-Purpose Filler Strategy
The formulation combines at least 5 phr of Al(OH)₃ with 10 phr or more of DCPD, CPD, or C5 resins. This combination creates a tread compound that remains stiff at normal operating temperatures while preserving the flexibility needed for low-temperature performance. The aluminum hydroxide serves a dual purpose: it reinforces the rubber matrix while acting as a heat sink that helps prevent dangerous high-speed blowouts.
Functionalized Interface Optimization
To optimize the polymer-filler interface, the system uses functionalized SBR grades with glass-transition temperatures ranging from −69°C to −20°C. These SBR polymers feature amino-silane or thiol end-groups that form chemical bonds with silica particles, reducing the Payne effect and enabling lower overall hysteresis. The result is a tread compound that delivers stronger grip on both dry and wet surfaces while achieving measurably lower rolling resistance compared to conventional formulations.
3.4. Ice-Optimized Butadiene Systems for Extreme Cold Performance
For extreme cold conditions below freezing, tire engineers shift their strategy toward butadiene-rich matrices that remain flexible at very low temperatures. Goodyear engineered an ice-centric BR Tg stratification system specifically designed for Nordic driving conditions.
Ultra-Low Temperature Matrix Design
The approach combines two distinct polybutadiene grades with dramatically different glass-transition temperatures: an ultra-low −80°C grade paired with a higher −20°C grade. To maintain rubber-like flexibility even on polished ice, formulators add substantial amounts of plasticizer—typically 40–120 phr of both mineral and vegetable oils.
This oil package prevents the rubber from becoming brittle in extreme cold while preserving the grip needed for ice traction. The silica coupling system uses 8–15 phr of silane coupling agent to ensure proper filler dispersion throughout the oil-extended matrix. The result is Nordic tires that deliver superior ice grip as their primary strength, while still maintaining strong performance across snow, wet, and dry road conditions.
3.5. Oil-Extended All-Season Versatility Systems
For applications requiring all-season versatility, Goodyear designed an oil-extended high-Tg S-SBR system that addresses multiple performance requirements simultaneously. The approach starts by pre-swelling the S-SBR with 5–40 phr of vegetable triglyceride oil, then blending it with high-cis polybutadiene rubber.
Dual-Function Oil Extension
This oil extension serves two purposes: it keeps the rubber flexible at low temperatures while providing the chemical compatibility needed for effective silica coupling. The manufacturing process includes an extended mixer silanization step that allows formulators to use only 3–6 phr of silane coupling agent—significantly less than conventional formulations.
Comprehensive Performance Benefits
This reduction in silane content lowers both material costs and energy loss during tire operation. The performance benefits are substantial: the storage modulus (G′) drops by up to 40% at −20°C, which translates to better flexibility on snow and ice. At the same time, tan δ at 60°C decreases, delivering improved fuel economy during normal driving conditions. The result is an all-season tread compound that performs well across the full range of temperatures and road conditions that drivers encounter throughout the year.
3.6. Managing Performance Evolution During Service Life
Even the most carefully engineered dual-Tg polymer systems face a practical challenge: their performance characteristics change as the tire operates. During driving, the tread compound heats up from repeated flexing and road friction, which alters its viscoelastic properties. At the same time, the tread surface gradually wears away, exposing deeper layers of rubber that may have different compositions or properties.
These changes can cause the tire's grip, rolling resistance, and handling characteristics to drift over its service life. To address this challenge, tire engineers have developed sophisticated radial and lateral layering strategies that maintain consistent performance as the tread heats up and wears down.
4. Radial and Lateral Layering for Temperature and Wear-Depth Management
4.1. Heat Distribution Through Dual-Conductivity Architecture
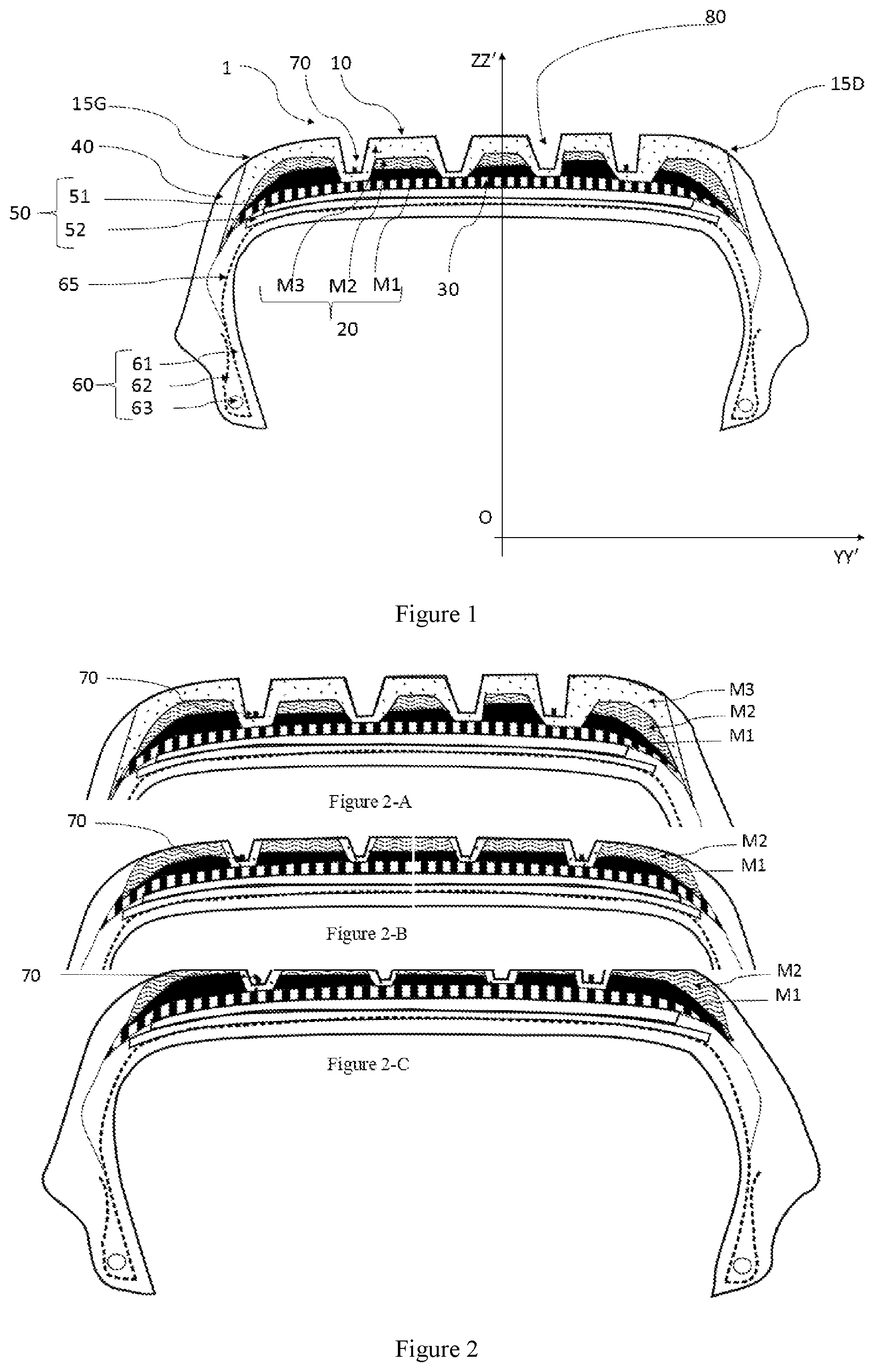
High-speed passenger car tires face a challenging problem: pressure and heat tend to concentrate in isolated zones during operation. Researchers at Sumitomo Rubber (a Japanese tire and rubber products manufacturer that operates the Falken and Dunlop brands in select regions) developed a solution called a dual-conductivity heat-drain architecture that addresses this issue through strategic material placement.
The design works by creating narrow islands of high-thermal-conductivity rubber that cover just 10–30% of the tire's contact area. These islands are embedded within a larger matrix made from low-conductivity, low-tan δ material. The islands function as internal heat sinks, drawing dangerous temperature peaks away from hot spots before they can cause damage. Meanwhile, the surrounding low-loss matrix maintains efficient rolling performance during normal driving.
When engineers combine this zoning approach with carefully controlled geometric limits on outer diameter and groove ratios, the results are impressive. The system delivers more than 10% improvements in both high-speed grip and overall durability compared to conventional tire designs. This dual-conductivity strategy allows high-performance tires to handle the extreme conditions of sustained high-speed driving while maintaining the fuel efficiency that drivers expect.
4.2. Winter Performance Through Progressive Compound Exposure
Winter tires face a unique challenge: they need to maintain grip on snow and ice even as the tread wears down over thousands of miles. Researchers at Michelin (French tire giant known for premium tires across segments and for the Michelin Guide's restaurant ratings) developed a solution using a snow-grip retention gradient that actually improves winter performance as the tire ages.
Layered Compound Strategy
The technology works by stacking three different rubber compounds in layers from the surface to the base of the tread. Each layer has a different cross-link density and plasticizer content designed for a specific stage of the tire's life. The key innovation lies in the middle layer, where sulfur and accelerator concentrations reach their maximum levels. This creates a highly cross-linked network that only emerges after the outer tread wears away.
As this aggressive middle compound becomes exposed, it provides the mechanical bite needed to grip compacted snow—exactly when conventional tires would be losing their winter performance. To prevent this stiffer compound from increasing rolling resistance, engineers incorporated a silica-rich filler system that limits energy loss during flexing. The innermost layer contains an ultra-low-Tg phosphate plasticizer that keeps the entire tread supple even in sub-zero temperatures, ensuring the tire remains flexible throughout its service life.
4.3. Life-Stage Adaptive Wet-Grip Systems
Tire manufacturers must meet strict regulatory standards for wet-braking performance throughout a tire's entire service life. This creates a challenge because conventional tires lose their wet-grip capabilities as the tread wears down, potentially falling below safety requirements long before reaching the legal wear limit.
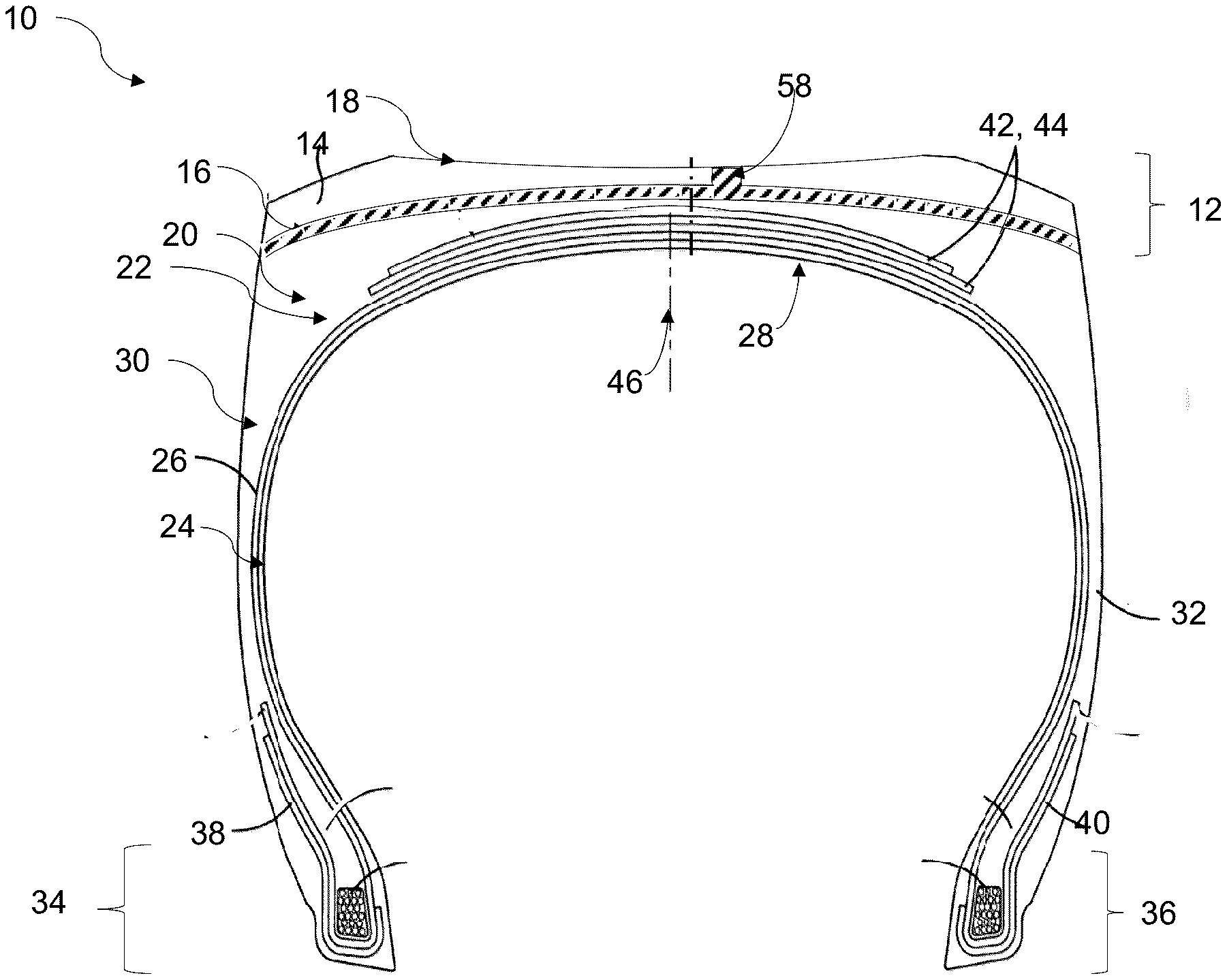
Michelin developed a solution called a life-stage adaptive wet-grip layer that maintains consistent wet-weather performance as the tire ages. Rather than using a single homogeneous tread compound, the design incorporates two strategically layered materials with different properties.
Two-Stage Performance Evolution
The system starts with a thick, low-loss outer compound that provides fuel efficiency during the tire's early life. Beneath this lies a thinner middle layer—comprising 10 to 33 percent of the total tread volume—made from a high-hysteresis compound designed specifically for wet grip. As the outer 4–5 mm of tread wears away through normal use, this softer, grippier layer gradually becomes exposed.
This exposure happens at exactly the right time: when conventional tires would be losing their wet-weather bite near the legal wear indicators. The emerging high-hysteresis compound restores the viscoelastic properties needed for effective water channeling and road contact, essentially giving the tire a "second life" for wet-grip performance.
Testing with prototype 245/45 R18 tire assemblies demonstrated that this approach successfully maintains new-tire wet-grip performance scores even in the worn state, while still meeting UNECE R117 rolling-resistance requirements. This allows tire manufacturers to design products that stay within regulatory compliance throughout their entire service life, improving both safety and consumer confidence.
4.4. Specialized Racing Applications
Thermal and Electrical Management in Racing Tires
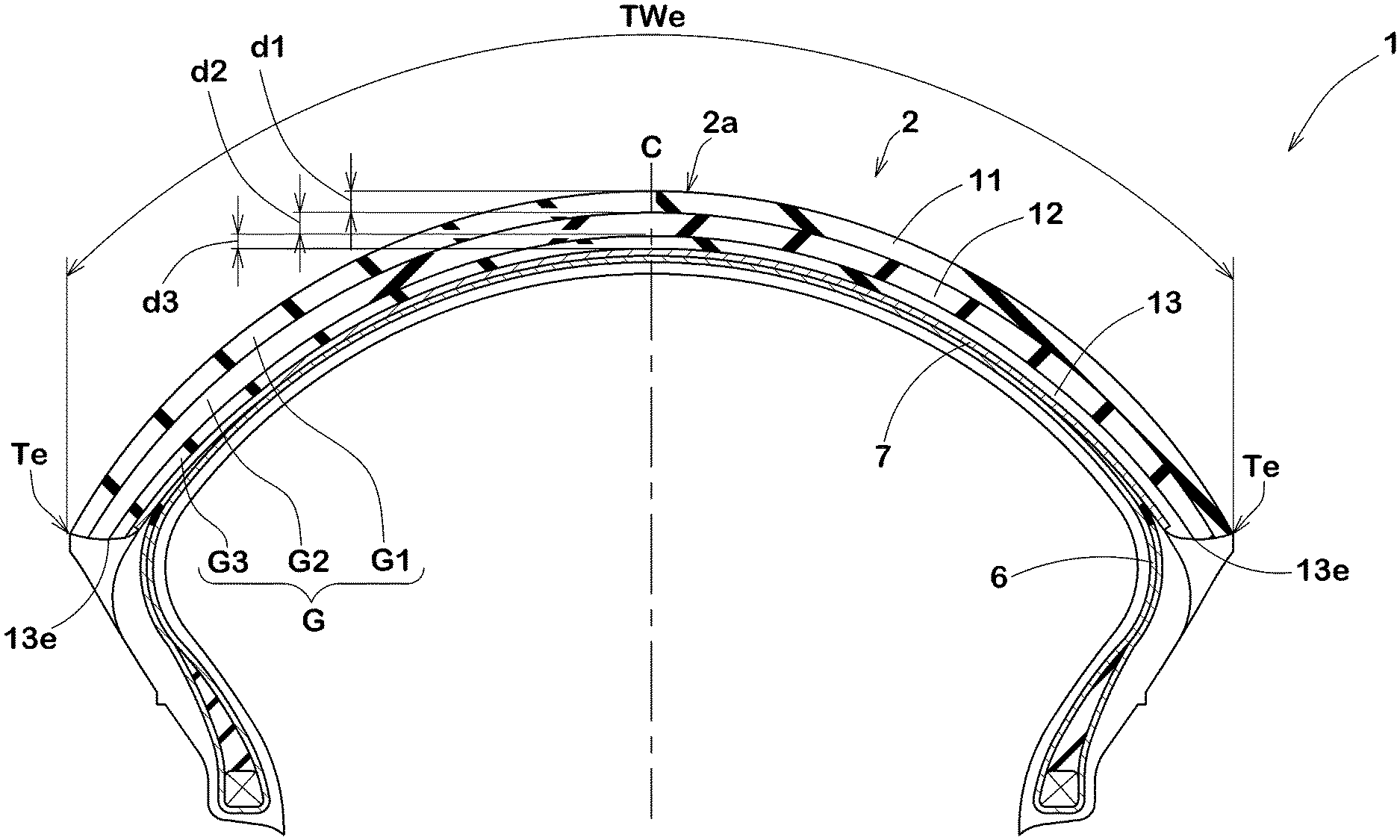
Racing tires face unique challenges beyond regular passenger cars: they must handle extreme thermal loads while also providing electrical grounding to dissipate static charge buildup. Goodyear came up with an innovative solution using a partially-exposed carbon-rich base that allows two different co-cured compounds to share the same contact footprint.
The design works by creating strategic windows in the tread surface that expose different materials depending on the performance requirement. The primary tread cap uses a silica/resin-loaded S-SBR compound optimized for maximum grip on both wet and dry track surfaces. However, carefully positioned openings in this cap reveal an underlying polyisoprene/carbon-black base compound that serves two critical functions: it acts as a heat sink to dissipate the extreme temperatures generated during high-speed cornering, and it provides electrical conductivity to safely channel static charge away from the tire.
This dual-compound approach allows racing teams to optimize their tire performance for specific track conditions. The grip-focused cap compound handles the primary contact duties, while the exposed carbon-rich base manages the thermal and electrical challenges that would otherwise limit tire performance or create safety hazards during competition.
Motorcycle Racing Wear Resistance
Motorcycle racing presents a unique challenge: tires must resist wear during aggressive cornering while still providing the precise feedback that riders depend on for control. Sumitomo Rubber developed an innovative solution called a viscoelastic inversion cap-base architecture that addresses both requirements simultaneously.
The design deliberately inverts the conventional approach by placing a lower tan δ compound with a colder glass-transition temperature on the surface, while positioning a higher-hysteresis sublayer underneath. This counterintuitive arrangement works because the surface compound experiences less internal shearing and generates less heat during operation, which significantly improves wear resistance. Meanwhile, the more energy-dissipative underlayer continues to provide the grip and tactile feedback that riders need when leaning into high-speed corners. The result is a racing tire that lasts longer without sacrificing the precise handling characteristics that are critical for motorcycle performance.
4.5. Structural Integration Considerations
While layered rubber compounds successfully manage temperature distribution and wear patterns throughout a tire's service life, they cannot address a fundamental challenge: maintaining stable contact with the road surface under varying loads and speeds. The contact patch—the small area where rubber meets pavement—must remain consistent in shape and pressure distribution to deliver predictable handling and braking performance. This stability depends on the structural framework that supports the tread compounds from beneath. The steel belts, textile cords, and underlying carcass architecture determine whether the carefully engineered rubber layers can maintain their intended contact geometry when subjected to the forces of acceleration, cornering, and braking. Without proper reinforcement design, even the most sophisticated dual-Tg polymer systems and adaptive layering strategies will fail to deliver their performance benefits consistently.
5. Belt Geometry, Cord Selection, and Airless Frameworks for Patch Stability
5.1. Controlled Crown-Belt Undulation for Passenger Cars
Passenger car tires traditionally use flat steel belt profiles, but this design can create handling and heat management problems. The flat geometry allows excessive rubber shear in the crown area and can lead to belt edge instability during aggressive cornering or high-speed driving.
Researchers at Michelin developed a solution using controlled crown-belt undulation that deliberately curves the belt structure instead of keeping it flat. The approach works by raising the metal belt crest at the tire's ribs by 1 mm or more, creating a controlled wave pattern across the crown area.
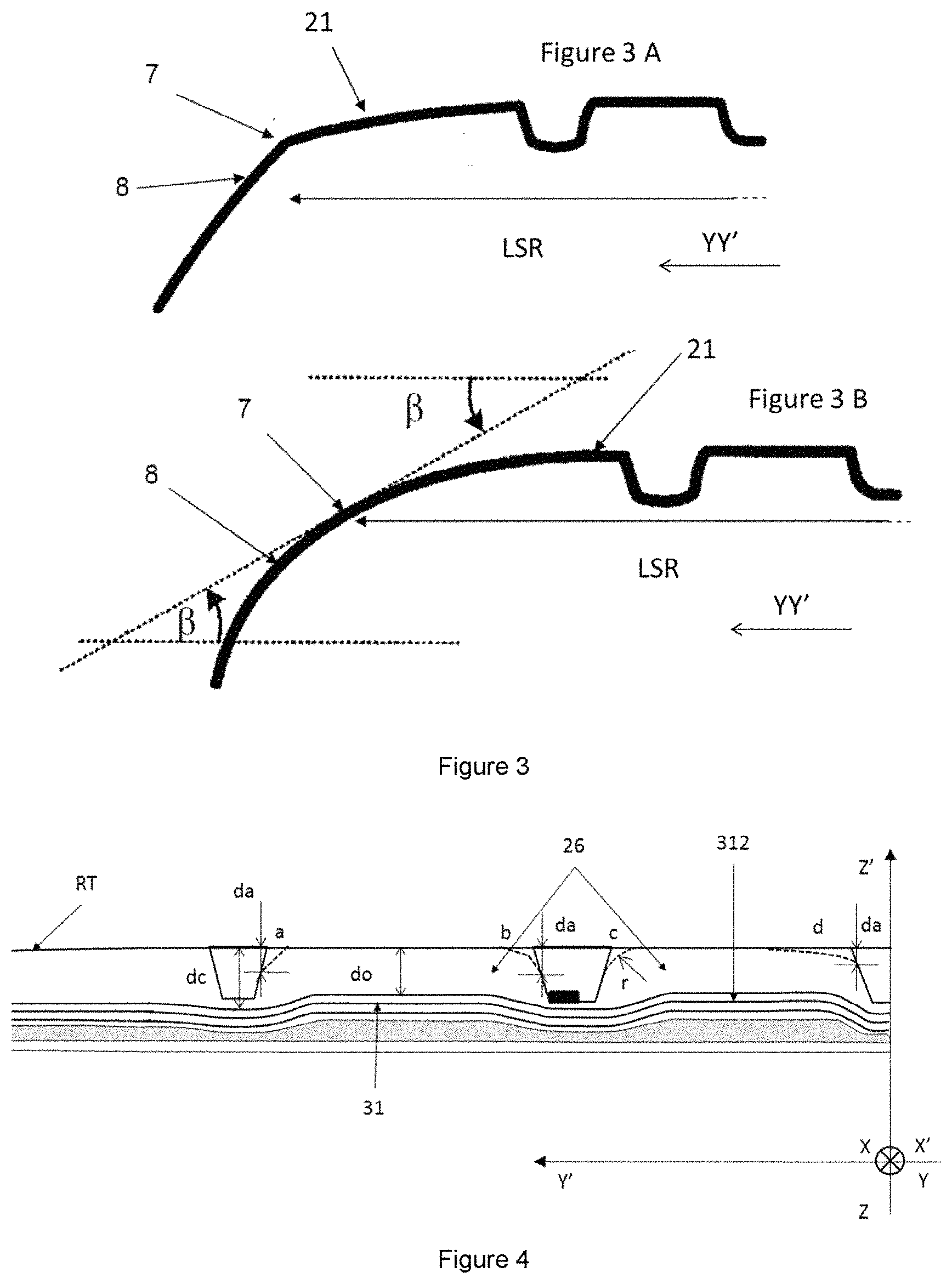
Performance and Manufacturing Benefits
This undulation strategy delivers several performance benefits. By reducing the effective shear thickness of rubber in the crown, it increases the tire's axial stiffness, which translates to sharper steering response. The curved belt geometry also prevents dangerous buckle-in failures at the crown edges that can occur during high-stress driving conditions. Additionally, the improved load distribution reduces heat buildup during sustained high-speed operation.
From a manufacturing perspective, the continuous cord package maintains its durability through standard fatigue testing cycles. The design works with existing flat building drums used in tire production, requiring only minor tooling inserts to create the undulated profile. This compatibility allows tire manufacturers to implement the technology without major capital equipment changes while delivering measurably better steering precision and thermal management.
5.2. Low-Strand Steel Cord Architecture for Motorcycles
Motorcycle tires face a unique engineering challenge: they need high tensile stiffness to handle the forces of acceleration and braking, yet they must bend smoothly to follow the curved tread profile without creating stress concentrations.
Sumitomo Rubber developed a solution using a low-strand steel cord architecture that carefully controls the cord construction. The design limits each cord to just one to three filaments per strand and two to six strands per cord overall.
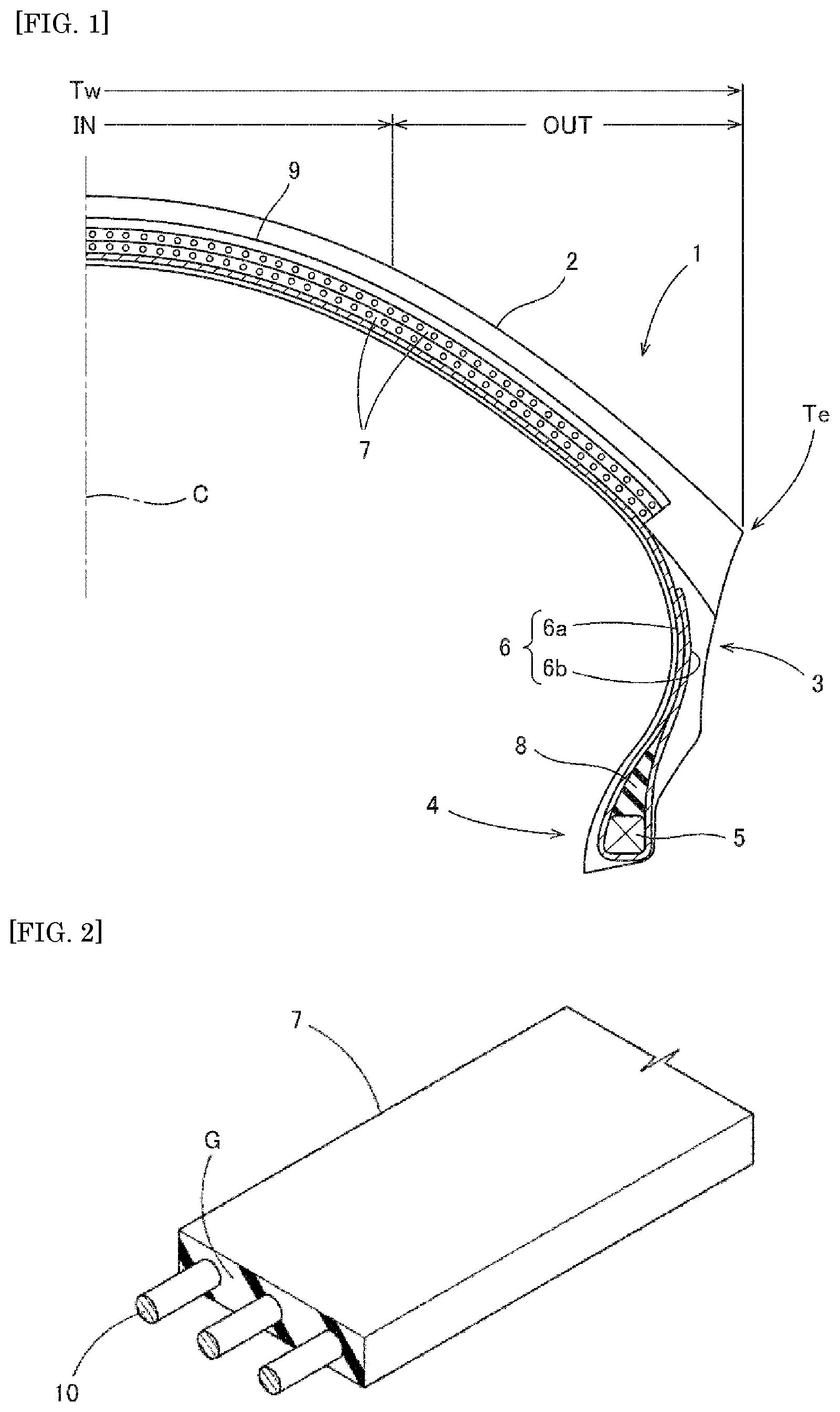
The key innovation lies in the precise specifications: filament diameters range from 0.15 to 0.25 mm, and all strands are twisted in the same direction. This identical twist direction is crucial because it allows engineers to fine-tune how the belt responds to compression and bending forces. The result is a belt that flexes smoothly to follow the motorcycle tire's curved tread profile without kinking or creating weak points.
When this cord system is paired with a tread compound whose complex modulus reaches approximately 5 MPa at 70°C, the combination eliminates the buckle waves that typically plague steel-belted motorcycle tires. The performance benefits are substantial: riders get the same precise steering response they would expect from premium aramid fiber belts, but at a significantly lower cost. This makes high-performance handling accessible to a broader range of motorcycle applications.
5.3. Belt-Band Hybrid Systems for Motorcycle Lean-Angle Optimization
Some motorcycles feel reluctant to lean into turns at shallow angles because their belt structure creates excessive hoop stiffness during initial lean-in. This phenomenon, known as hoop-stiffness overshoot, makes the bike feel rigid and unresponsive during gentle cornering maneuvers.
Sumitomo Rubber addressed this issue with a belt-band hybrid layout that strategically combines different belt architectures. The design uses one inner bias belt ply and one outer bias belt ply that sandwich a near-circumferential band ply between them.
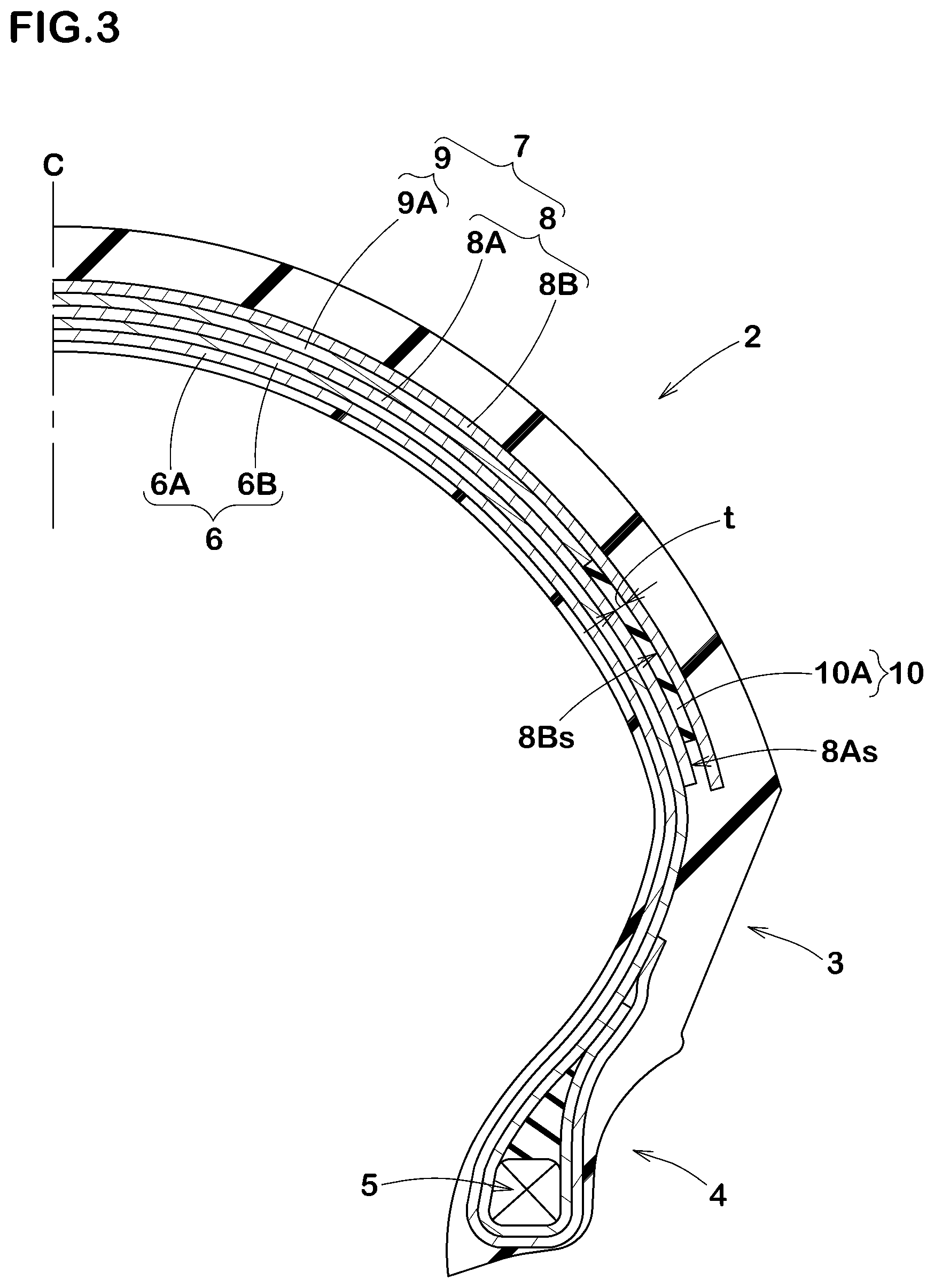
The key to the system's performance lies in its graduated width design: the outer belt extends slightly wider than the inner belt, while the band width falls between the two. This creates a structure that provides radial support exactly where it's needed during aggressive high-lean cornering, while allowing easier roll-in during gentle turns at low camber angles.
The performance benefits are substantial: motorcycles equipped with this belt-band hybrid system show improved gentle-turn metrics, making them more responsive and natural-feeling during everyday riding. At the same time, the design extends tire endurance life by better managing stress distribution across different riding conditions.
5.4. Segmented Spoke Assembly for Airless Tire Frameworks
Airless tires face a fundamental challenge: without air pressure to maintain shape, the structural framework must provide all the support needed for stable road contact. Researchers at Kenda (a Taiwanese tire maker offering value-oriented tires for bicycles, motorcycles, passenger vehicles and specialty applications) developed a solution using a segmented spoke assembly that redesigns the internal support structure entirely.
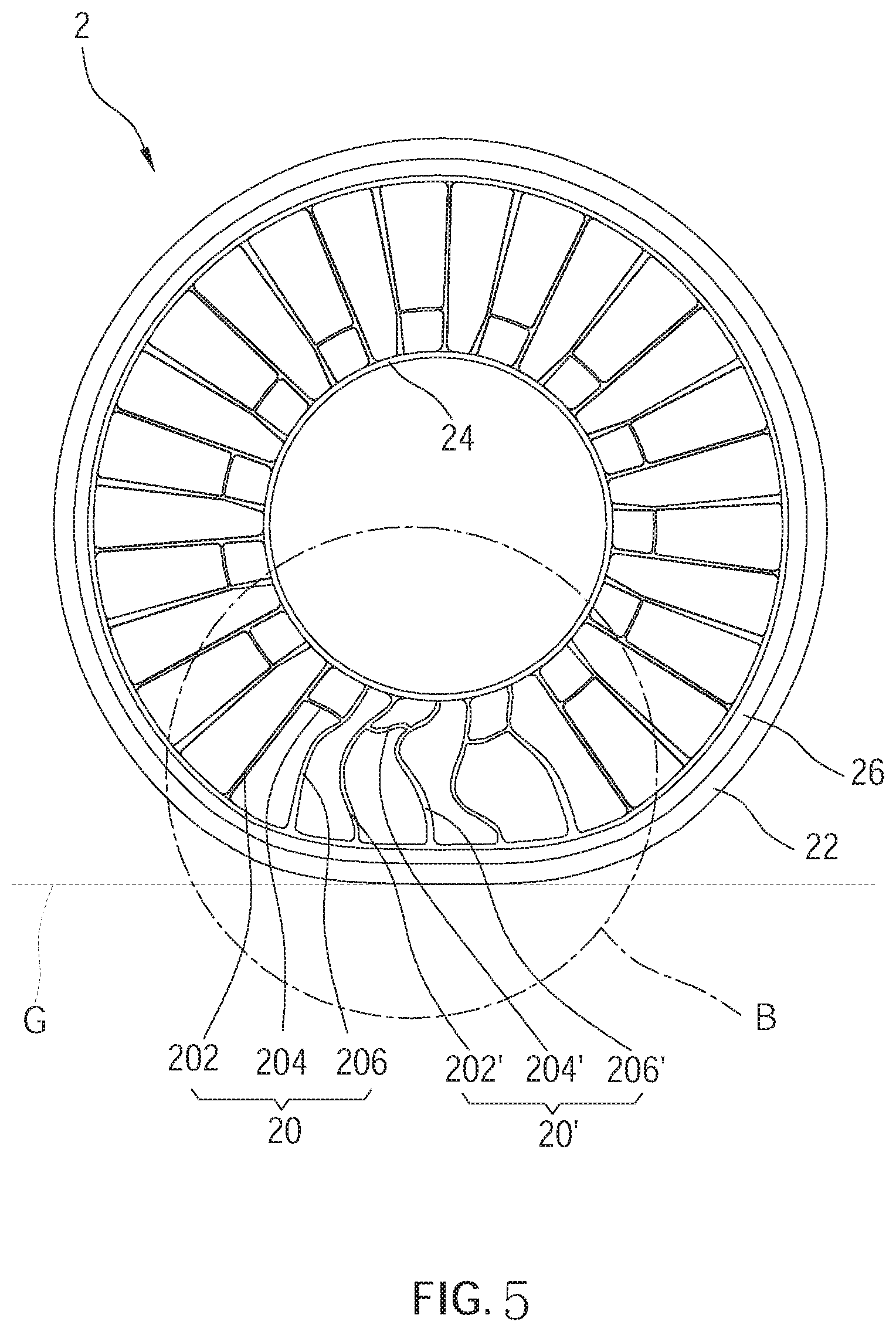
Eliminating Spoke Friction Through Controlled Deformation
The approach reorganizes each spoke into three distinct components: a straight spoke section, a bent spoke with two non-colinear segments, and a connecting linking rib. This segmented design addresses a critical durability problem that has long plagued non-pneumatic tires. In conventional airless designs, adjacent spokes often rub against each other when the tire compresses under load, creating frictional wear that gradually weakens the structure and limits tire life.
The segmented geometry prevents this destructive contact by controlling how the spokes deform during compression. Instead of allowing random contact between neighboring spokes, the bent segments and linking ribs guide the deformation in a controlled manner. This eliminates the frictional wear that previously made airless tires impractical for extended use, while maintaining the contact-patch stability needed for consistent handling and braking performance.
Transitioning to Water Management Challenges
While structural frameworks ensure that tread compounds maintain stable contact with the road surface, they cannot solve a critical safety challenge: removing water from between the tire and pavement during wet-weather driving. Even the most sophisticated dual-Tg polymer systems and adaptive layering strategies will fail to provide adequate grip if water becomes trapped in the contact patch. When a layer of water separates the rubber from the road surface, the tire loses its ability to generate the friction needed for safe braking and cornering. This means that the groove patterns, channels, and drainage features carved into the tread surface play an equally important role in wet-weather performance as the advanced rubber compounds beneath them.
6. Hydrodynamic Groove Engineering for Consistent Wet Braking
6.1. Stepped Groove Architecture for Wear-Resistant Drainage
Grooves that retain water-evacuation capacity over the entire tread life start with a stepped design approach. Bridgestone developed stepped circumferential main grooves that use a dual-depth architecture to maintain drainage performance as the tire wears.
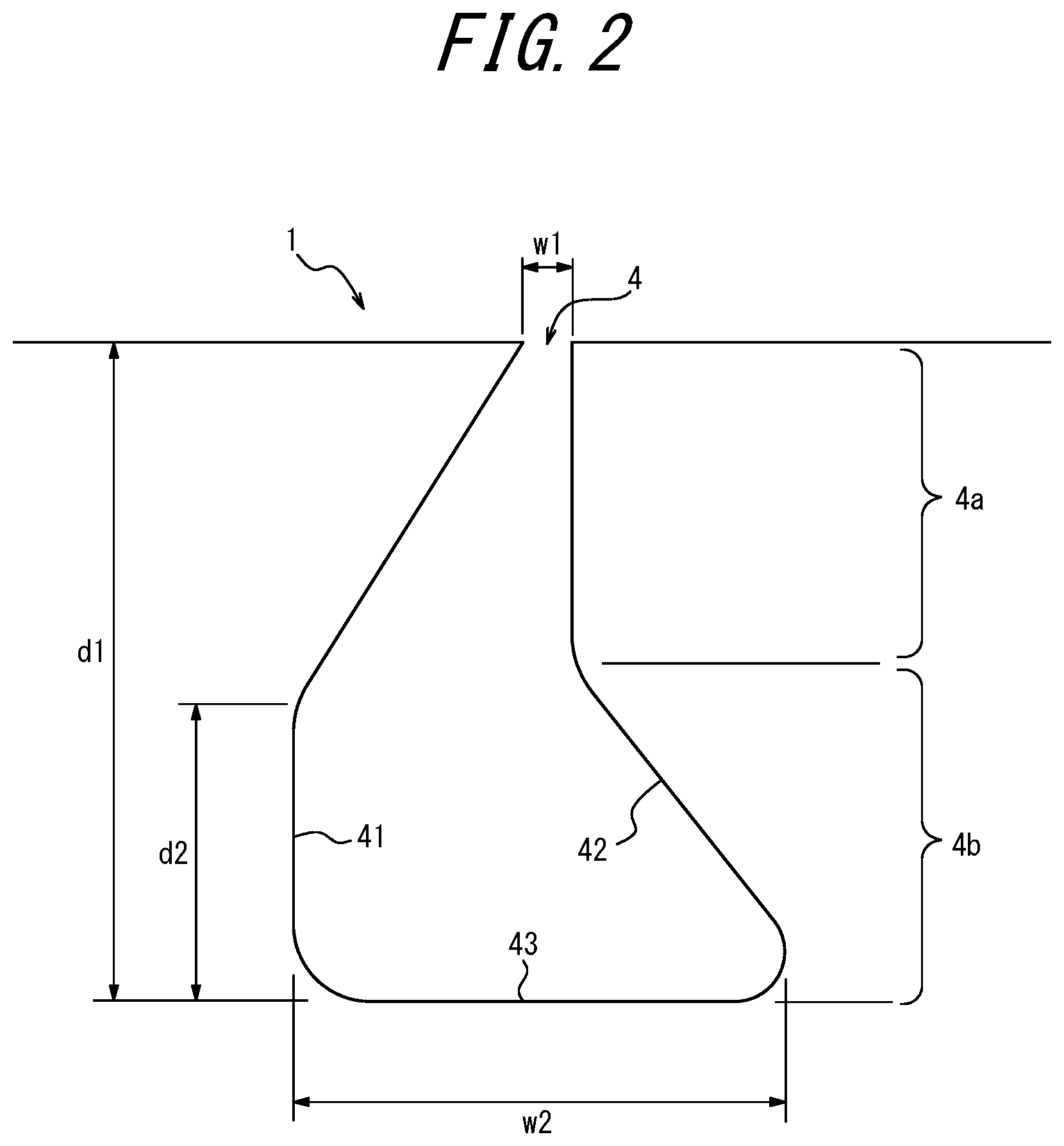
The system works by creating two distinct drainage zones within each main groove. A shallow outer step positioned near the tread surface handles water evacuation during the tire's early life, clearing edge water before it can build up in the contact patch. Meanwhile, a deeper inner step continues to provide drainage capacity even after several millimeters of tread have worn away through normal use.
This dual-zone approach ensures that hydro-planing resistance remains nearly constant throughout the tire's service life. Because the deeper section stays active until the tire reaches its legal wear limit, drivers experience consistent wet-weather performance rather than the gradual degradation typical of conventional groove designs.
6.2. Complementary Depth-Width Hierarchies
Depth must pair with width to optimize water evacuation performance. Researchers at Yokohama (a Japanese tire and industrial rubber products maker known for ADVAN and Geolandar lines) developed a depth–width hierarchy of main and lateral grooves that uses opposite sizing strategies for different groove types.
The design philosophy specifies that main circumferential channels should be deeper than lateral grooves, while lateral grooves are engineered to be wider than the mains. This creates complementary drainage functions: the deep but relatively narrow circumferential grooves handle longitudinal water flow and provide space for wear indicators, while the shallower but broader lateral grooves efficiently vent water sideways out of the contact patch.
To complete the system, engineers add micro-sized sipes that close under load. These tiny channels provide additional biting edges for traction when the tire contacts the road, but they compress shut during rolling to suppress the air pumping noise that would otherwise create unwanted exterior sound. The result is a groove architecture that maximizes wet-weather drainage while maintaining quiet operation throughout the tire's service life.
6.3. Multi-Directional Water Escape Routes
Path orientation adds another variable to water evacuation strategies. Researchers at Toyo Tire developed a lattice of oppositely angled longitudinal and lateral grooves that creates trapezoidal tread blocks designed to present effective gripping edges regardless of the direction of force.
The crossed geometry works by multiplying the number of shear edges available for traction while simultaneously forming converging corridors that funnel water away from the contact patch center during high-speed driving. This dual-angle approach ensures that water has multiple escape routes rather than being trapped between conventional parallel grooves, which can lead to hydroplaning during aggressive wet-weather driving conditions.
6.4. Zoned Performance Optimization
Ultra-high-performance programs also demand block rigidity for dry grip. To address this challenge, tire engineers split the tread band into specialized zones that optimize both water evacuation and structural stiffness. Researchers at Pirelli (Italian manufacturer focused on high‑value consumer tires for cars and motorcycles; the exclusive Formula 1 tire supplier since 2011) developed a zoned approach where wide shoulder areas host transverse grooves that flare outward, rapidly ejecting water laterally during wet-weather driving.
Meanwhile, continuous annular ribs positioned between these grooves keep both the shoulders and central ribs structurally stiff for precise dry-road handling. The key to this design lies in carefully calibrated void-to-rubber ratios: approximately 0.25 in the shoulders to maximize water drainage capacity, and 0.20 in the narrow central zone to prioritize block rigidity. This balance ensures that the tire can channel water effectively during wet conditions while maintaining the structural integrity needed for high-performance dry grip.
6.5. Active Water Steering Through Block Edge Design
Wet braking distances shrink further when the block edges themselves steer the water. Bridgestone developed differentially chamfered lateral groove ends that replace blunt sidewalls with angled micro-channels designed to actively direct water flow.
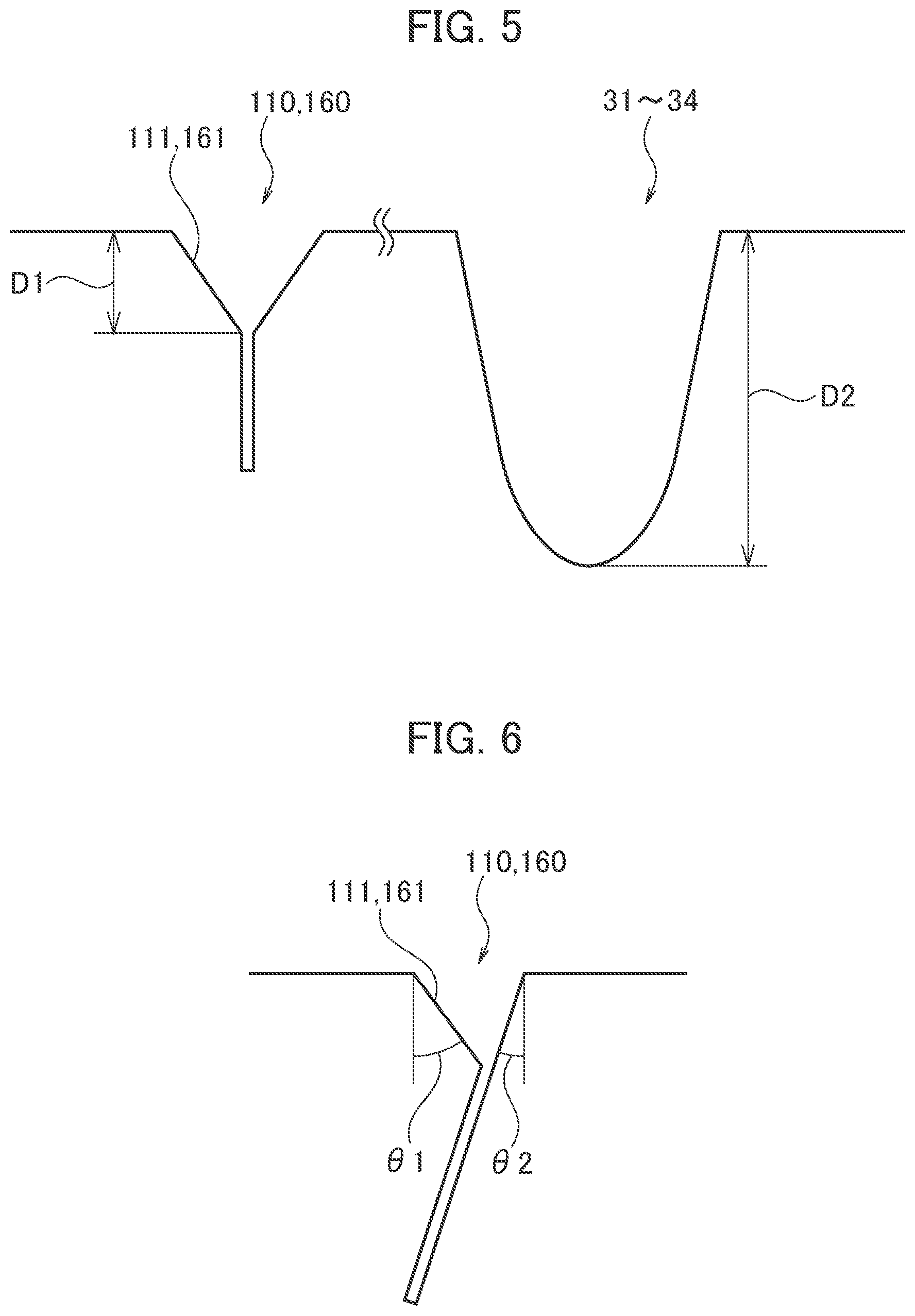
The system uses two different chamfer angles on opposite sides of each groove opening. A steeper first chamfer acts like a scoop, capturing water and directing it into the groove during braking forces. Meanwhile, a gentler opposite chamfer maintains the structural integrity of the tread block while still allowing water to exit efficiently. This dual-angle approach ensures that water gets actively channeled away from the contact patch rather than simply being displaced randomly, improving wet-weather braking performance without compromising the block stiffness needed for precise handling on dry roads.
6.6. Microscopic Water Management Through Sipes
While groove patterns handle the bulk water evacuation needed to prevent hydroplaning, they cannot address a more subtle challenge: maintaining grip on wet or snow-covered surfaces where thin films of moisture remain between the tire and road. These conditions require a different drainage strategy that works at the microscopic level.
Sipes—the thin slits carved into tread blocks—create thousands of tiny biting edges that can penetrate through surface moisture to contact the pavement beneath. Unlike the larger grooves that channel bulk water away from the contact patch, sipes function as micro-squeegees that wipe away the residual water films that would otherwise cause the tire to slip. This micro-level water management becomes the determining factor for sustained wet-weather traction and snow grip throughout the tire's service life.
7. Depth-Managed Sipe Networks for Long-Life Snow and Wet Grip
Current OEM specifications often demand tread features that regenerate as the tire wears down over thousands of miles. This creates an engineering challenge: how to maintain grip-enhancing features without compromising the structural integrity of fresh tread blocks.
7.1. Three-Level Adaptive Architecture
Bridgestone designed a three-level adaptive sipe architecture that addresses this challenge through strategic depth management. The design divides each sipe into three distinct segments: shallow surface slots, intermediate-depth channels, and deep base sections.
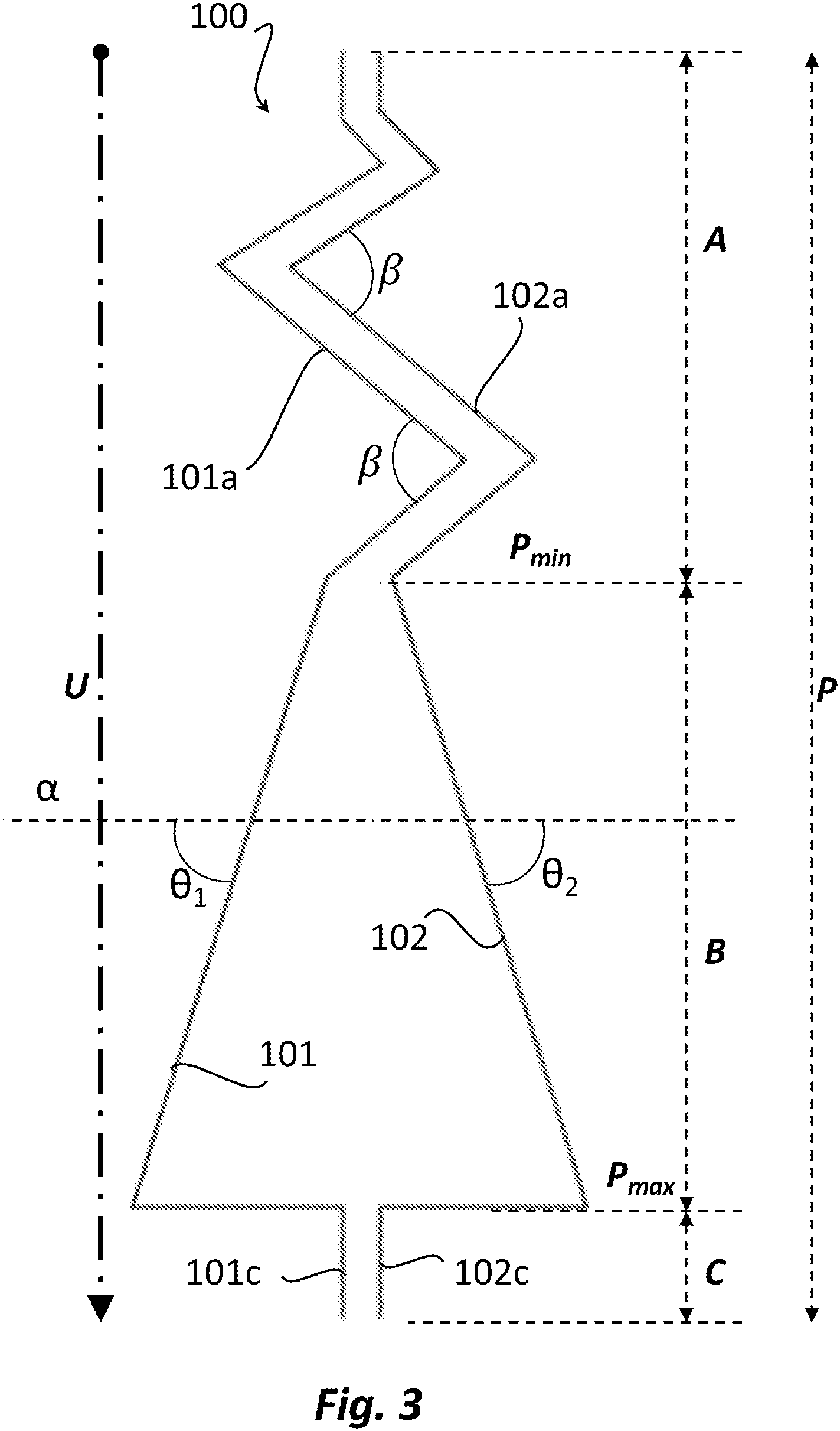
On a new tire, only the uppermost tier remains open to preserve block rigidity during aggressive dry-road driving. As the tread wears through normal use, the deeper tiers gradually become exposed and begin to widen progressively. This controlled exposure refreshes both the void volume needed for water evacuation and the biting edges required for snow traction, essentially giving the tire renewed grip capabilities as it ages.
The key advantage lies in manufacturing simplicity: the progressive widening happens naturally through wear rather than requiring complex mold geometries or specialized tooling. This allows tire manufacturers to deliver regenerating tread features without significantly increasing production costs or complexity.
7.2. Depth-Graded Zig-Zag Positioning
Snow and ice traction depends heavily on creating enough biting edges to penetrate through surface layers and grip the underlying pavement. While void volume helps with bulk water evacuation, the density and positioning of these edges often determines whether a tire can maintain control on slippery surfaces.
Researchers at Yokohama developed a solution using a depth-graded zig-zag sipe that strategically positions grip-enhancing features where they're most effective. The design places the peak amplitude of each zig-zag pattern at 30–60% of the sipe's total depth, rather than at the surface where conventional designs typically locate their maximum edge density.
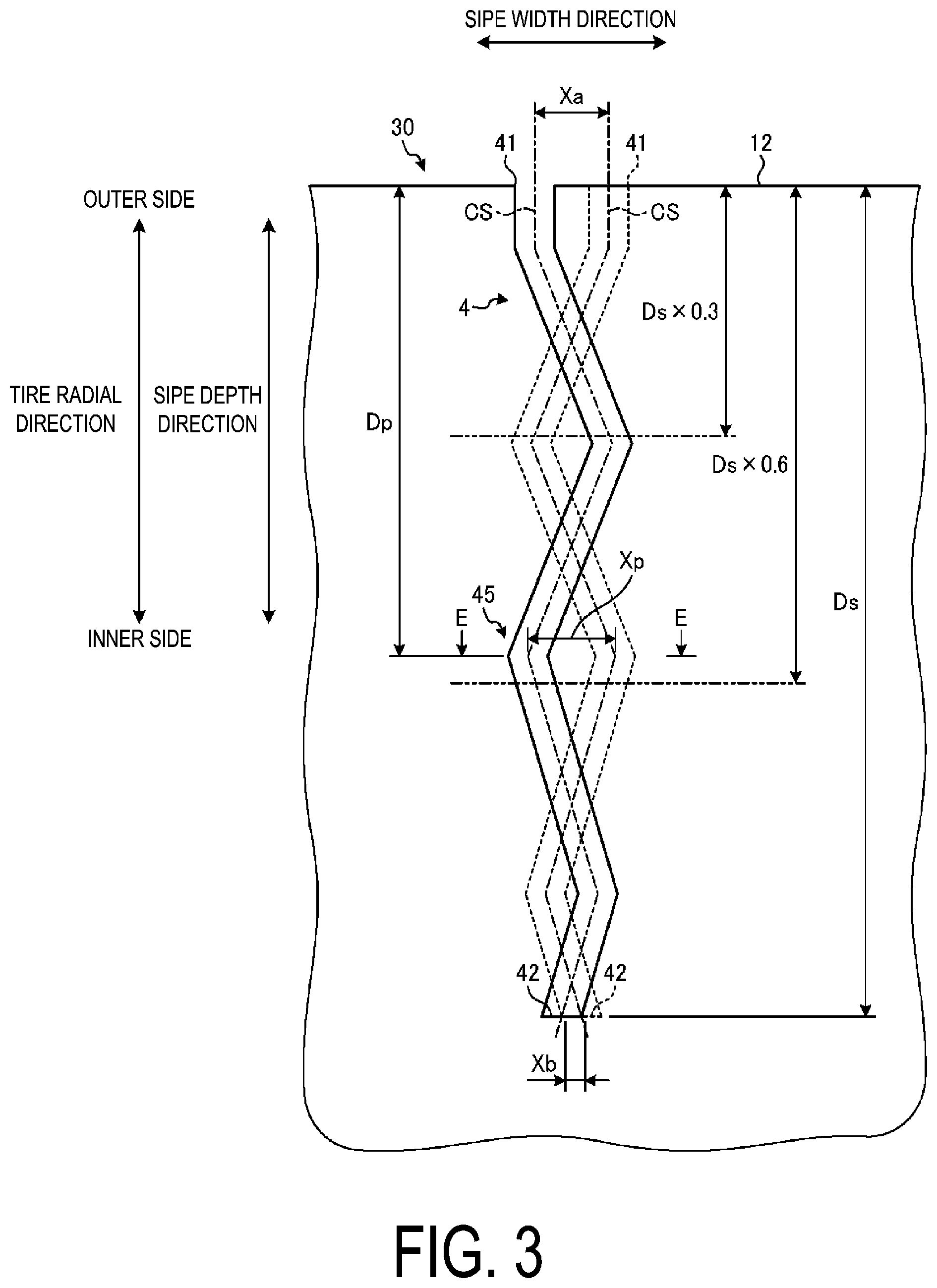
This depth-graded approach delivers performance benefits that evolve as the tire wears. On a new tire, the reduced amplitude near the surface helps maintain block stiffness during dry-road driving, preventing excessive deformation that could compromise handling precision. As the tread wears down through normal use, the deeper sections with peak zig-zag amplitude become exposed, creating fresh shear edges that can interact effectively with packed snow and ice. The result is a tire that actually improves its cold-weather grip capabilities as it ages, maintaining winter traction throughout its service life rather than losing performance as the original surface features wear away.
7.3. Chamfer-Based Stiffness Optimization
Tire engineers need to balance competing demands when designing sipes: they must create enough biting edges for wet traction while preserving the structural rigidity needed for precise handling. Traditional sipe designs often compromise one requirement to achieve the other.
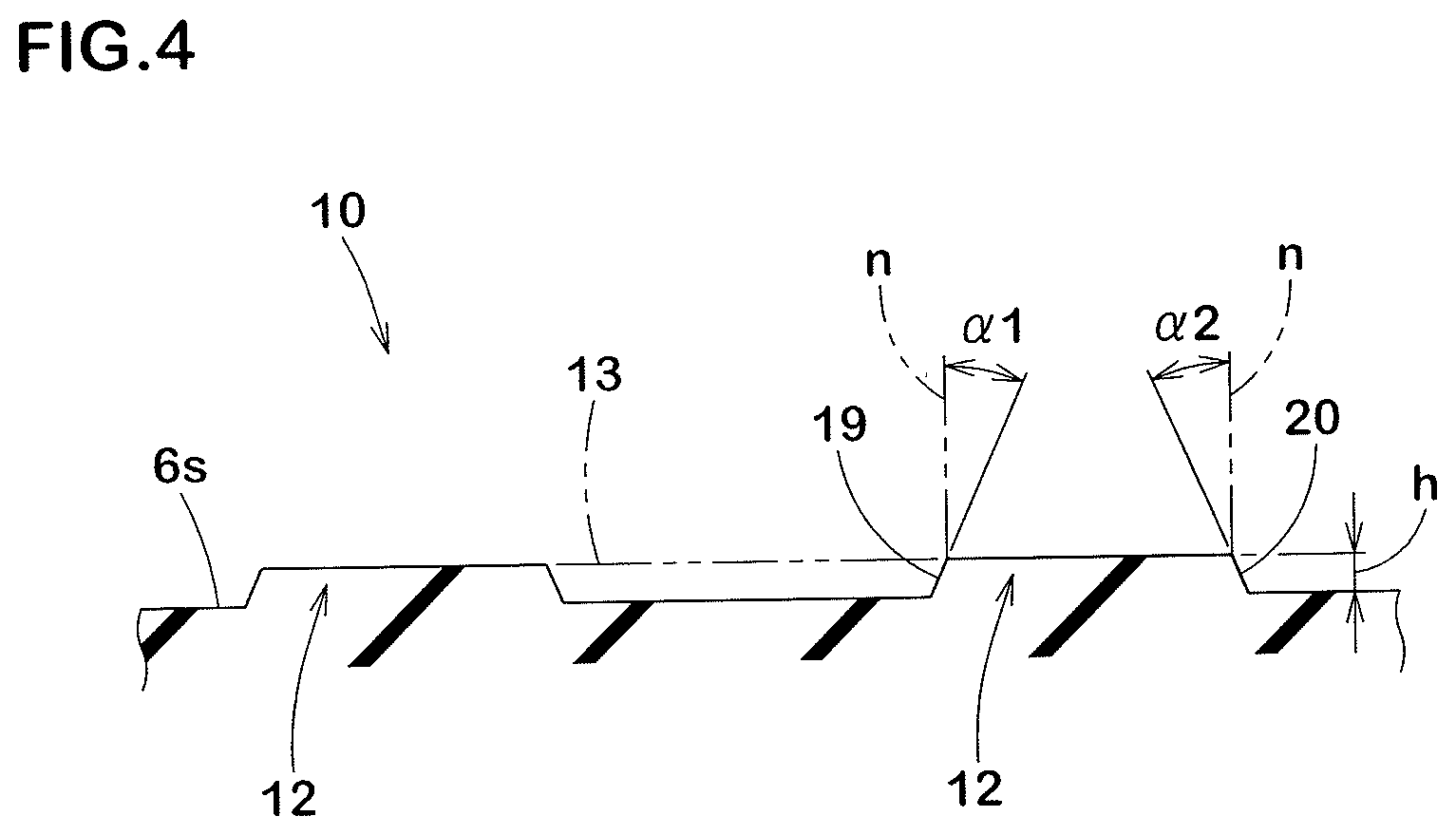
Selective End Chamfering
Yokohama developed a targeted solution using selectively-chamfered rib sipes that address this challenge through strategic geometry control. Rather than chamfering the entire length of each sipe, the design restricts the wedge-shaped reliefs to only the leading and trailing ends of each slot.
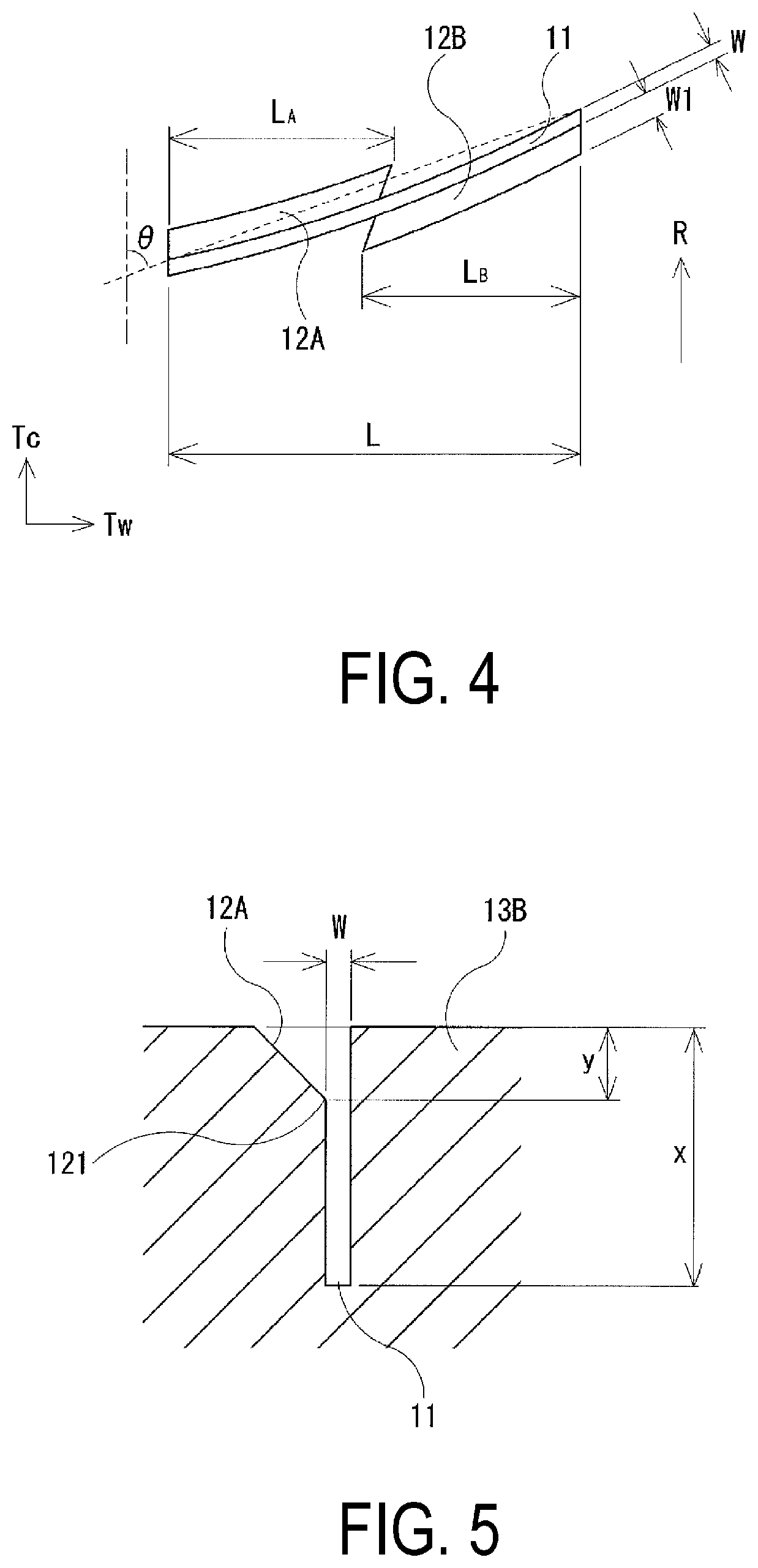
This selective approach delivers the best of both worlds. The unchamfered middle section preserves the bending and torsional rigidity that drivers need for precise steering response during dry-road driving. Meanwhile, the chamfered ends maintain enough edge effect to provide effective wet braking performance when water is present on the road surface.
Progressive Shoulder Applications
For shoulder applications where noise control becomes critical, Yokohama developed a complementary approach called the progressive shoulder-edge chamfer. This design gradually reduces the chamfer thickness as it approaches the tire's outer edge, creating a tapered profile that serves dual purposes.
The progressive geometry prevents the shoulder blocks from lifting away from the road surface during cornering, which maintains consistent contact pressure for better grip. Additionally, the tapered chamfer reduces the resonance noise that typically occurs when sipes open and close during rolling, creating a quieter ride without sacrificing the wet-weather traction that drivers depend on for safety.
7.4. Central Rib Differential-Depth Design
Central ribs face a unique engineering challenge: they must provide structural stiffness for precise steering while still offering adequate drainage for wet-weather safety. These competing requirements are particularly difficult to balance because conventional sipe designs typically optimize for one performance aspect at the expense of the other.
Researchers at Continental (German technology company and major tire manufacturer that also supplies automotive electronics, safety systems and industrial products) developed a solution using a differential-depth cavity sipe that addresses both requirements through strategic depth variation. The design combines a shallow central slot with deeper edge portions that open into mini-cavities connecting to the circumferential grooves.
This graduated depth approach delivers performance benefits that persist throughout the tire's service life. The shallow central section maintains the structural integrity needed for responsive handling during dry-road driving. Meanwhile, the deeper wing sections continue to reach through surface water films to contact the pavement beneath, even after substantial tread wear has occurred. The result is a central rib design that preserves both steering precision and wet-weather safety throughout the tire's operational life.
7.5. Multi-Dimensional Snow Cornering Networks
Snow-cornering degradation presents a particular challenge for winter tires because conventional straight sipes lose their effectiveness as the tread stiffens with wear. The blocks become more rigid over time, reducing the tire's ability to generate the lateral biting edges needed for grip on packed snow during cornering maneuvers.
Sumitomo Rubber developed a solution using a multi-region 3-D sipe network that addresses this degradation through strategic geometric design. The system places a near-surface axial element that connects to deeper circumferential arms hidden within each tread block.
This multi-dimensional approach works by compensating for the natural stiffening that occurs as tires wear. When the tire is new, the surface axial element provides the primary gripping function. As the tread ages and becomes more rigid through use, the deeper circumferential arms begin to flex more actively, generating fresh lateral edges exactly when they're needed most. The result is a sipe network that maintains its ability to grip low-friction surfaces like packed snow and ice far longer than conventional straight sipes, preserving winter cornering performance throughout the tire's service life.
7.6. Transition to Off-Road Applications
While groove patterns and sipe networks successfully manage water evacuation and snow traction on paved surfaces, they cannot address the challenges that off-road tires face when encountering loose soil, thick mud, and rocky terrain. These extreme conditions require a fundamentally different approach to tread design—one that focuses on mechanical penetration and self-cleaning rather than fluid drainage.
Unlike the thin water films that sipes can wipe away or the bulk water that grooves can channel, loose soil and mud present substantial mechanical resistance that must be physically displaced or penetrated. Rocky surfaces demand aggressive edge contact that can grip irregular contours and withstand impact loading. These requirements call for three-dimensional block and lug architectures that can dig into soft surfaces, shed sticky materials, and maintain structural integrity under the extreme forces encountered during off-road driving.
8. 3-D Block and Lug Architectures for Extreme-Terrain Traction
8.1. Circumferentially Linked Shoulder Systems for Snow Traction
Snow tires often struggle with straight-line bite in the shoulder area, where conventional block designs fail to provide adequate grip on packed snow. Addressing this challenge, Sumitomo Rubber developed a solution using a circumferentially linked shoulder protrusion system that combines the drainage benefits of narrow shoulder blocks with the structural stiffness of continuous ribs.
The design works by extending radially oriented ribs outward from each shoulder block, then connecting these protrusions through an inner circumferential rib that bridges across selected lateral grooves. This creates a hybrid architecture that functions like individual blocks for water evacuation while behaving like a continuous rib for structural support.
The linked protrusions deliver multiple performance benefits for winter driving. They create fresh biting edges that can penetrate through surface snow layers to grip the pavement beneath. The continuous connection also resists the twisting forces that typically cause shoulder blocks to deform during acceleration and braking, allowing them to generate higher snow-compaction forces for better traction. Importantly, the design maintains the lateral groove openings needed for hydroplaning resistance and preserves the tire's ability to generate lateral grip during cornering maneuvers.
8.2. Agricultural Stubble-Ejecting Lug Protection
Agricultural tires face a persistent problem when working in harvested fields: sharp stalk stubble can chip away pieces of the tread lugs, gradually reducing their effectiveness. This damage typically occurs at the outer wing of each lug, where the rubber first contacts the stubble during field operations.
To combat this issue, researchers at Michelin developed a solution using a leading-face stubble-ejecting discontinuity that protects the lugs from this type of damage. The design works by carving a shallow angled notch into the nose of each lug, creating a controlled weak point that actually strengthens the overall structure.
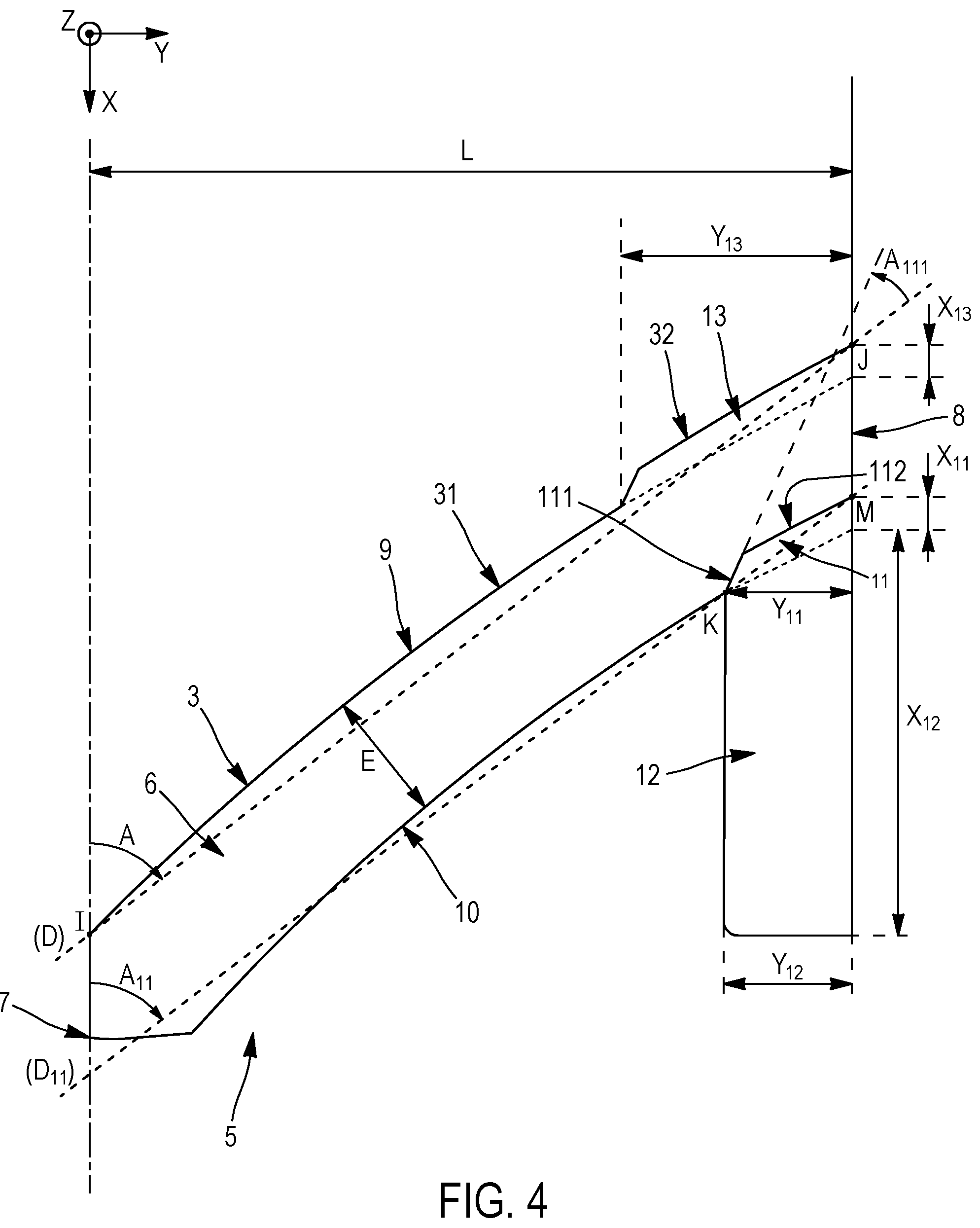
The notch starts at 20–50% of the lug's total height and angles downward to end in a bottom recess. This geometry serves a dual purpose: it provides an escape route for crop stalks that would otherwise get trapped and cause chunking, while also creating a channel for soil release that prevents mud buildup. The key advantage is that this protective feature preserves the lug's core thickness and maintains its ability to generate traction in soft field conditions, extending tire life while keeping agricultural equipment productive during critical harvest and planting seasons.
8.3. Multi-Layer Block Architecture for Mixed Off-Road Conditions
Off-road passenger and light-truck tires face a challenging engineering problem: they must provide effective grip on both jagged rocks and soft mud, two surfaces that require completely different tread characteristics. Sharp rocks demand durable edges that won't chip under impact, while soft mud requires aggressive lugs that can penetrate and self-clean.
Step-Shaped Crown Blocks with Chamfered Protection
Sumitomo Rubber researchers tackled this challenge using step-shaped crown blocks with full-circumference chamfer that addresses both requirements through a sophisticated three-layer architecture.
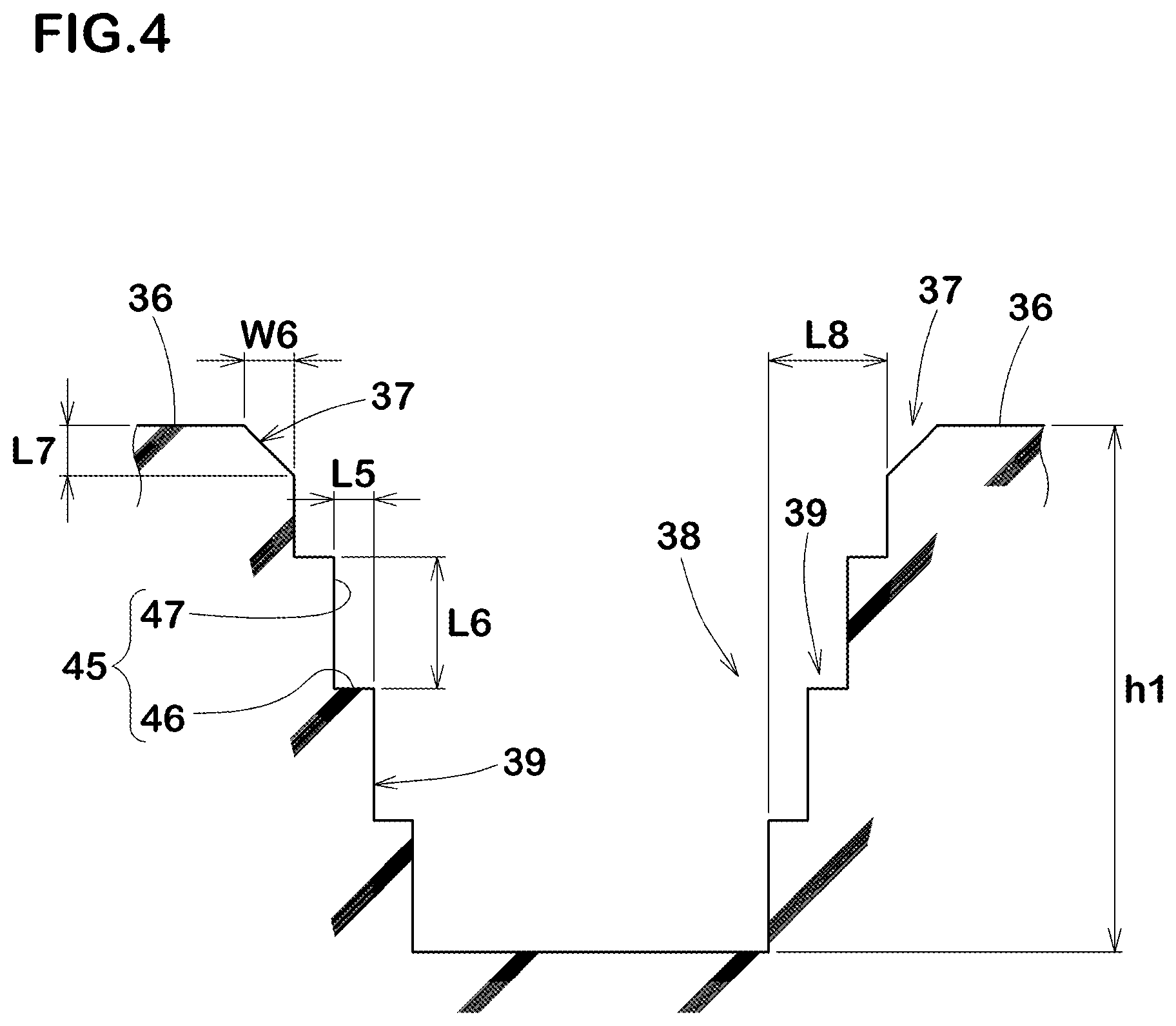
The design works by creating multiple levels of grip elements within each tread block. A peripheral chamfer around the entire block edge serves as the first line of defense, distributing impact stress to prevent chipping when the tire contacts sharp rock edges. Beneath this protective outer layer, an internal staircase structure creates a series of micro-lugs that can adapt to different terrain types as the tire wears.
This hierarchical approach delivers the best of both worlds. The stepped internal geometry multiplies the number of biting edges available for traction in soft surfaces like mud and loose soil. At the same time, the chamfered perimeter shields the block's structural core from the impact damage that typically occurs during rock crawling. The result is an off-road tire that maintains its aggressive traction capabilities while resisting the chunking and chipping that would otherwise limit its service life in extreme terrain conditions.
Two-Stage Shoulder Support for Trials Motorcycles
Trials-style motorcycles operate at low air pressures and extreme lean angles, creating a significant risk of shoulder block collapse during aggressive riding. The unstable blocks can fold over under load, causing sudden loss of grip on technical terrain.
Sumitomo Rubber engineers developed a solution using a two-stage shoulder block with mountain support that addresses this stability problem through strategic internal reinforcement.
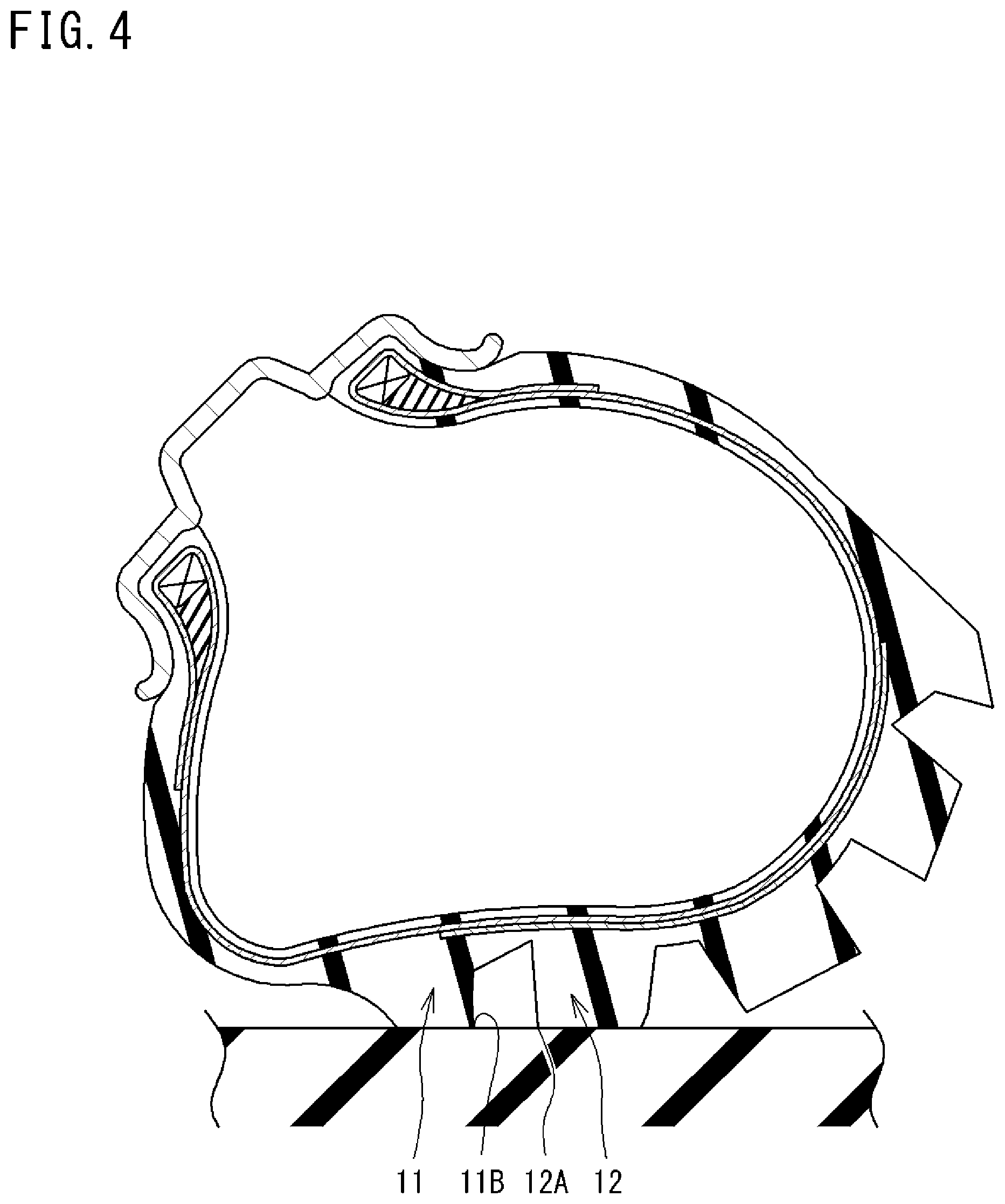
The design works by allowing the shoulder tread surface to protrude 0.5–5 mm beyond the tire's normal profile, creating an aggressive contact patch for maximum grip on rocks and roots. However, rather than leaving these extended blocks unsupported, the system incorporates a hidden internal "mountain" structure that occupies at least five percent of each block's total volume. This internal reinforcement acts like a skeleton, preventing the block from collapsing inward when subjected to the extreme side loads that occur during steep lean angles.
The controlled stiffness gradient between the flexible outer surface and the rigid internal support ensures that the tire maintains full-width contact with jagged terrain while resisting the structural failure that would otherwise limit performance during technical riding. This allows trials riders to maintain traction and control even when navigating challenging obstacles at extreme lean angles.
Concave Tripod Blocks for Heavy Construction
Heavy construction vehicles need lugs that can penetrate deep mud while surviving the abrasive punishment of rocky terrain. Michelin researchers developed a solution using concave tripod-style penetration blocks that deliberately invert the conventional convex lug design.
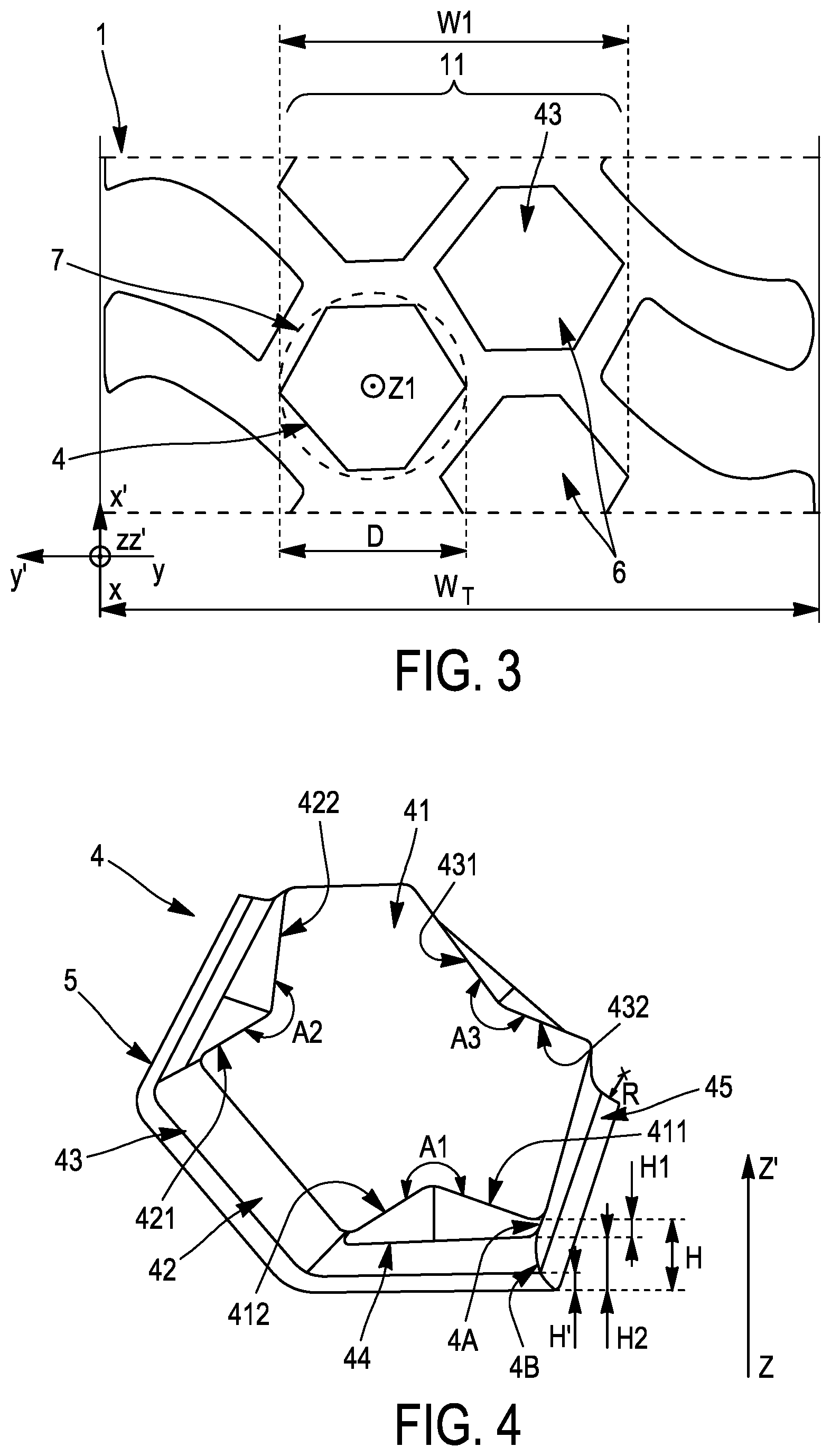
The innovative approach works by creating each block with a concave face featuring three interior angles greater than 180°. This unusual geometry forms a trident of sharp edges that can dig aggressively into soft mud and soil. The concave shape also reduces the loaded contact area, which concentrates the vehicle's massive weight into smaller pressure points for better penetration through challenging terrain.
To handle the extreme forces generated by thirty-ton construction equipment, the design incorporates a wider convex base that anchors each block to the tire carcass. This broader foundation distributes the mechanical stress across a larger area, preventing the lugs from tearing away under the heavy loads and high torques that construction vehicles generate during excavation and grading operations. The result is a tread design that delivers aggressive off-road traction without sacrificing the durability needed for demanding construction applications.
8.4. Dual-Scale Groove Matrix for Deep-Snow Performance
Deep-snow automobile tires face a challenging design trade-off: they need wide channels to evacuate packed snow, but these same channels can weaken the tread blocks and reduce structural rigidity. This creates problems with forward traction and uneven wear patterns that limit tire performance in winter conditions.
Engineers at Yokohama developed a solution using a dual-scale main and sub lug groove matrix that addresses both requirements through strategic sizing differences. The design alternates very wide, very deep primary grooves with much narrower secondary grooves that measure only ten to thirty-five percent as wide as the main channels.
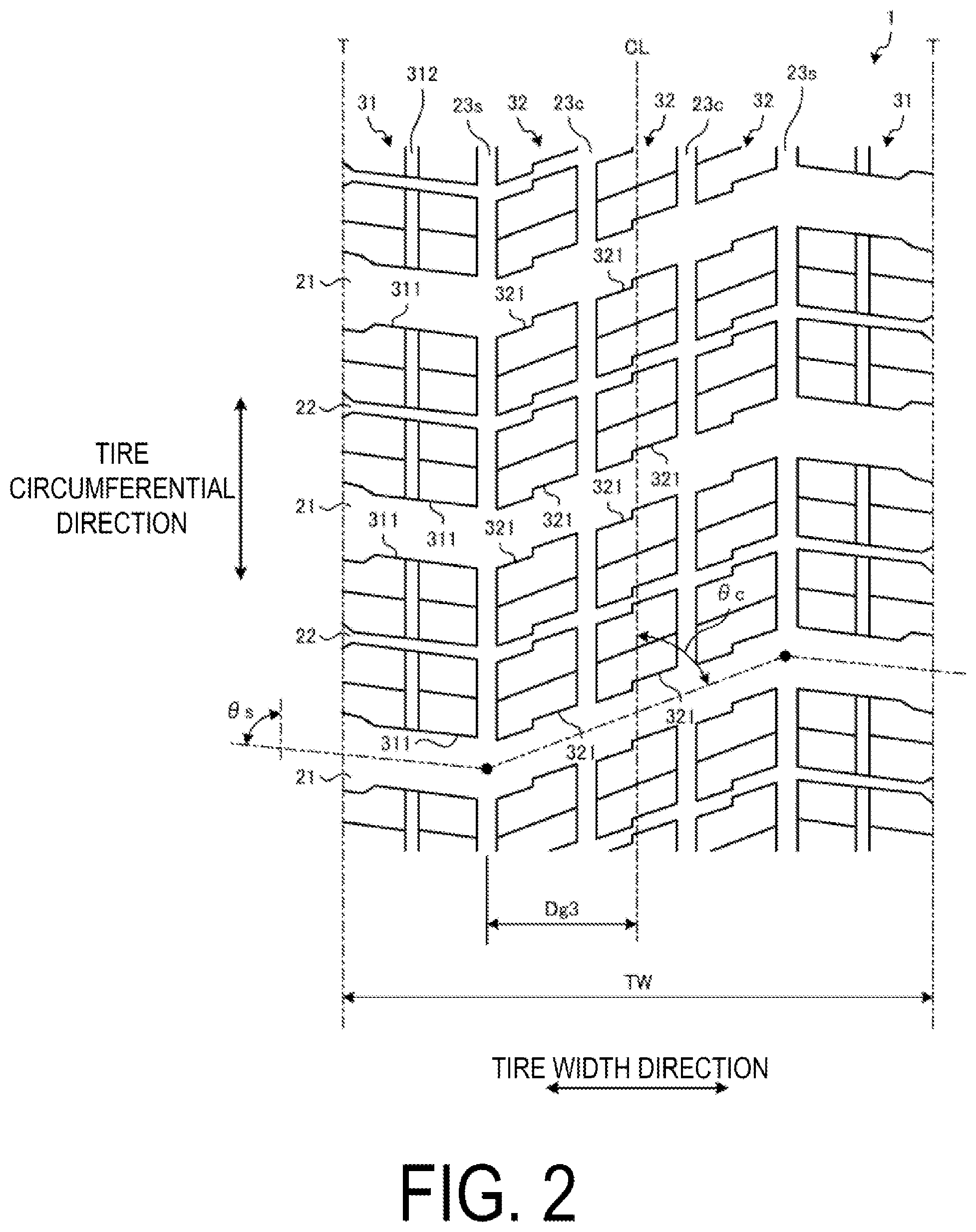
This dual-scale approach delivers complementary performance benefits. The wide primary channels handle the bulk snow evacuation needed to prevent packing and maintain grip on deep snow surfaces. Meanwhile, the slim secondary cuts multiply the number of biting edges available for traction without significantly weakening the structural integrity of each tread block. The result is improved forward traction and more uniform wear patterns throughout the tire's service life, giving drivers better control and longer-lasting performance in challenging winter driving conditions.
8.5. Integrated Design Philosophy
These advances in polymer chemistry, structural engineering, and tread geometry work together to create a comprehensive toolkit for tire design. Engineers can now combine dual-Tg rubber matrices with fractal-controlled silica networks, then add progressive layering strategies and sophisticated drainage patterns to match almost any driving condition. Whether the challenge is maintaining wet grip as the tread wears down, delivering consistent snow traction throughout the tire's life, or providing aggressive off-road bite without sacrificing durability, the integrated approach allows precise tuning of performance characteristics. The result is tires that can be optimized for specific applications—from fuel-efficient passenger cars to heavy construction equipment—while maintaining the balance of competing requirements that real-world driving demands.
Get Full Report
Access our comprehensive collection of 195 documents related to this technology
Identify Key Areas of Innovation in 2025

